
Collagen for Loose Skin: Does it Tighten Skin? Supplements and Tips
Collagen for Loose Skin
In the quest for healthy, youthful skin, the spotlight has turned to collagen – the protein powerhouse that lies at the core of our skin's structure.
Collagen is the key to maintaining skin elasticity, firmness and that coveted radiant glow. If you've ever wondered how to harness the transformative power of collagen, you're in the right place.
In this article, I delve deep into the science of collagen and it's profound impact on skin health. From its role in combating aging to its ability to address common skin concerns, we’ll explore the fascinating world of collagen and its benefits for your skin.
So, buckle up and prepare to unlock the secrets of collagen, as we guide you on a journey toward youthful, luminous skin.
Before we dive in, I have to mention that if you are looking for a product recommendation, the single best source of collagen for skin is a high protein bone broth.
More on that later, for now, let's dive in.
Collagen and Skin Health: What Does the Science Say?
A vast review of human studies of collagen conducted in the Dermatology Practical & Conceptual in 2022 found extensive evidence that collagen supplements improve skin moisture, elasticity and hydration. It also made skin smoother (1).
When I tried incorporating collagen into my skincare routine, I noticed huge improvements in the health and appearance of my skin.
I've dealt with various skin concerns in the past, but as I get older my loose skin has really bothered me. Collagen has been a game-changer for me. When I dug into the science, I found lots of reasons why.

Collagen and Skin Elasticity
One of the key benefits of collagen is its ability to promote skin elasticity. A study published in Plastic and Aesthetic Research in 2020 states that collagen is an essential protein to make skin smooth and give it elasticity (2).
As we age, our natural collagen production declines, leading to sagging skin. By supplementing with collagen or using collagen-infused skincare products, we can replenish and support our skin's collagen levels, resulting in firmer and more youthful-looking skin.
What's the Deal with Skin Hydration
But collagen doesn't stop at improving elasticity. It also helps to hydrate the skin, making it appear plumper and smoother. A study published in the American Journal of Pathology in 2006 found that reduced synthesis of collagen results in the appearance of chronologically aged skin (3).
Collagen molecules have a unique ability to bind with water, enhancing the skin's moisture retention. This can be especially beneficial for those struggling with dry or dehydrated skin. I've personally noticed a significant improvement in my skin's hydration levels since incorporating collagen into my routine.
Sagging Skin Tone Benefits
Another fascinating aspect of collagen is its potential to support the reduction of age spots and hyperpigmentation. Collagen helps to regulate melanin production, the pigment responsible for skin coloration.
A study published in Food & Function in 2020 found that collagen may be able to protect the skin against photoaging (4). By maintaining optimal collagen levels, we can potentially minimize the appearance of dark spots and achieve a more even skin tone.
I prefer collagen as a supplement, but studies overwhelmingly support its use as an injection. Drinking bone broth has made a huge difference in my aging skin, and I HATE needles.
But if you want a dramatic quick fix, lots of studies like the one published in Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology in 2017 found that injecting collagen precisely is a safe way to treat signs of aging with collagen (5).
My favorite part about collagen is its overall impact on skin health. By strengthening the skin's barrier function, collagen helps to protect against external aggressors, such as UV radiation and pollution.
It can also assist in healing wounds and reducing inflammation, promoting a healthier complexion. Making collagen a part of my everyday routine has made a huge impact on my skin, both signs of aging like sagging and my overall complexion.
Why does skin lose elasticity as we age?
As we age, the natural process of aging takes a toll on our skin, leading to a loss of elasticity. Understanding why this happens can shed light on the importance of collagen in maintaining youthful-looking skin.
One of the main factors behind the loss of skin elasticity is a decrease in collagen production. Collagen, a protein found abundantly in our skin, provides structure and support.

It acts like a scaffold, keeping our skin firm and resilient. However, as we get older, our bodies produce less collagen and the existing collagen fibers start to break down. This gradual decline in collagen leads to a loss of skin elasticity and the formation of wrinkles and sagging.
Another contributing factor to the loss of elasticity is the depletion of elastin fibers. Elastin is another protein that gives skin its elasticity and allows it to stretch and bounce back. Over time, the production of elastin decreases, causing the skin to lose its ability to recoil and recover its original shape.
Here are a few things that decimate collagen and elastin fibers:
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal changes such as a decline in estrogen levels during menopause
- Sun exposure
- Smoking
- Pollution
- Poor lifestyle habits
All of these things accelerate their breakdown and contributing to premature aging.
Does collagen help with loose skin?
Loose skin often occurs as a result of a decrease in collagen production and the breakdown of existing collagen fibers. Collagen is essential for maintaining the structural integrity and elasticity of the skin. When collagen levels decline, the skin becomes less firm and more prone to sagging.
In my experience, incorporating collagen into my routine has made a noticeable difference. The best supplements for sagging skin is definitely collagen, in my humble opinion.
By supplementing with collagen or using collagen-infused skincare products, you can help support and replenish your skin's collagen levels.
This, in turn, can improve the appearance of loose skin. Collagen works by stimulating the production of new collagen fibers and enhancing the skin's elasticity. It helps to restore the skin's firmness, making it appear tighter and more lifted.
In my opinion, combining collagen supplementation with regular exercise, a balanced diet and a comprehensive skincare regimen can yield the best results in addressing loose skin. Additionally, it's essential to be patient and consistent with your collagen routine, as results may take time to become noticeable.
How to Maximize Collagen's Skin Building Benefits
You can turbo charge collagen's skin benefits by lifting weights, taking vitamin C, getting good sleep and limiting sun exposure. Let's go through each of these in detail.
Lift Weights
Engaging in strength training exercises can promote collagen production. When you lift weights or perform resistance exercises, it stimulates the production of growth factors that support collagen synthesis.
This can contribute to improved skin elasticity and firmness. Incorporate weightlifting or resistance training into your fitness routine a few times a week to reap the skin-building benefits.

You want to take your collagen 30 minutes to one hour before you exercise or lift weights for best results. The exercise of loading of your joint is what helps to move the amino acids into your skin, joints and tendons.
Take it with Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a vital nutrient for collagen synthesis. It plays a crucial role in the formation of collagen fibers and protects existing collagen from damage.
When taking collagen supplements or consuming collagen-rich foods, combining it with vitamin C can enhance its effectiveness. Citrus fruits, berries, leafy greens and supplements can provide you with an ample supply of this essential nutrient.
Sleep
Getting enough quality sleep is vital for overall skin health, including collagen production. During sleep, your body goes into repair mode and collagen synthesis is heightened. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to optimize the skin-building benefits of collagen.
Limit Sun Exposure
Prolonged sun exposure can accelerate collagen breakdown and impair collagen production. UV radiation damages collagen fibers and promotes the production of enzymes that break down collagen.
Protect your skin by wearing sunscreen, seeking shade and using protective clothing, especially during peak sun hours. This helps minimize collagen damage and supports healthier, more youthful-looking skin.
How to Keep Your Collagen in Your Skin
You can do a few extra things to keep collagen levels high in your skin:
|
Methods for Boosting Collagen |
Summary |
|
Drinking Bone Broth |
Consuming it provides your body with essential amino acids like proline, glycine and hydroxyproline, which are vital for collagen production and skin structure support. |
|
Using Collagen Peptides Supplements |
Collagen peptides are smaller, easily absorbable forms of collagen. Consuming a supplement derived from reliable and sustainable sources can help in collagen synthesis and improve skin health. |
|
Reducing Alcohol |
Alcohol can dehydrate the body and impair the absorption of essential nutrients necessary for collagen synthesis. |
|
Quitting Smoking |
Smoking can damage collagen fibers, impair production, and restrict blood flow to the skin causing nutrient deprivation. |
Drink Bone Broth for Gut Health
Drinking delicious, easy to mix bone broth is my favorite way to get plenty of collagen in my diet.
If you're new to it, bone broth is made by simmering animal bones and connective tissues for an extended period. This slow cooking process allows the release of various nutrients, including collagen.
When you drink it, the collagen in bone broth is broken down into amino acids, which serve as building blocks for collagen synthesis in our bodies.
Drinking bone broth gives your body rare amino acids proline, glycine and hydroxyproline, which are essential for collagen production. These amino acids are vital components for forming collagen fibers and supporting skin structure.
Bone broth is full of other nutrient like potassium, hyaluronic acid and magnesium that can support overall skin health.
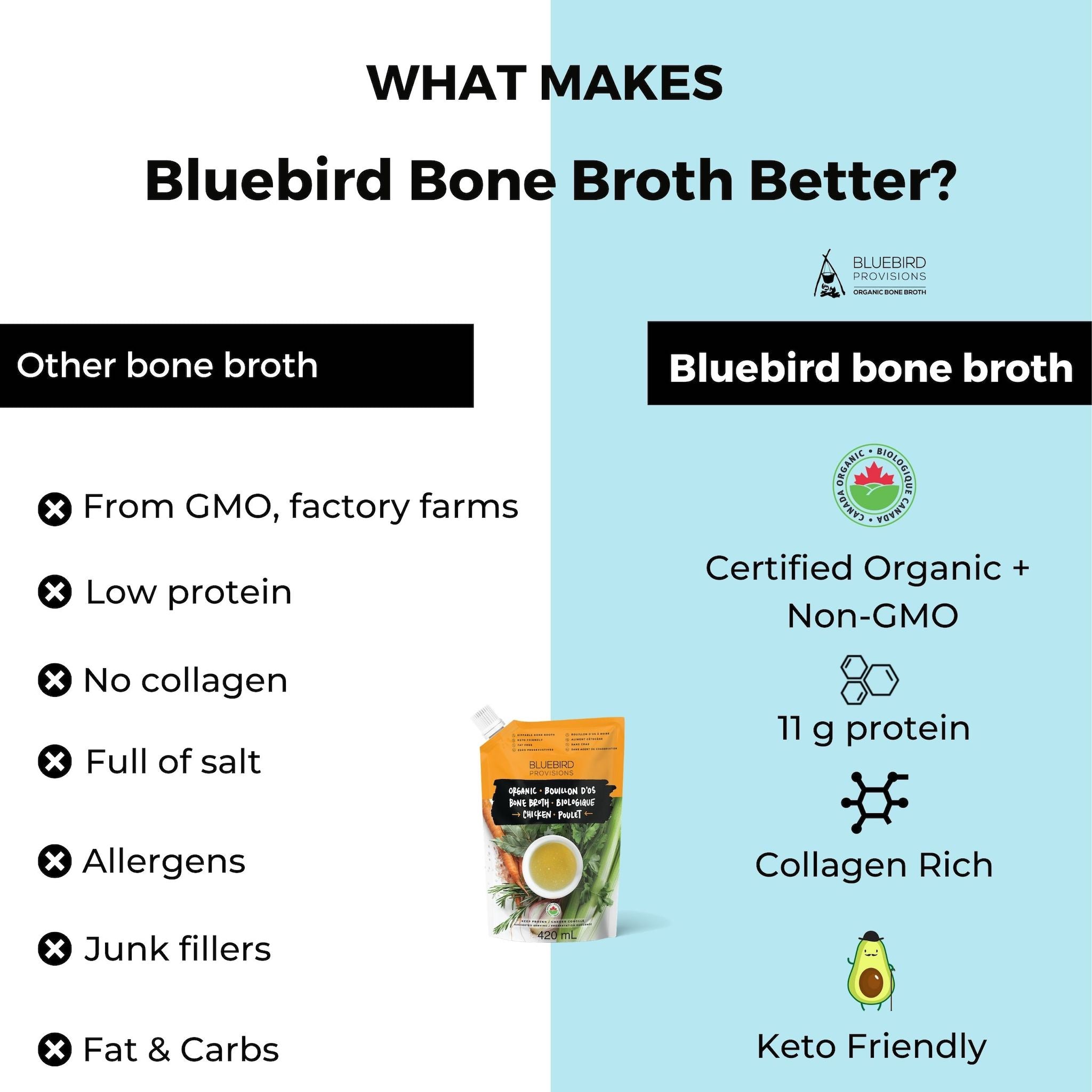
My favorite option is the chicken bone broth powder from Bluebird Provisions. You can find it on their website or on Amazon Prime for free shipping.
Try a Collagen Peptides Supplement
Collagen peptides are small, easily absorbable forms of collagen that are broken down into shorter chains of amino acids. When consumed as a supplement, these peptides can be efficiently absorbed by the body and transported to the skin, where they can contribute to collagen synthesis.

Look for a collagen peptides supplement from a reputable brand that sources its collagen from reliable and sustainable sources. Ensure that the product undergoes rigorous testing to guarantee its quality and safety.
Read my guide to finding the best collagen peptides powder for product recommendations based on your goals.
Reduce Alcohol and Smoking
Excessive alcohol intake can negatively affect collagen production and accelerate collagen breakdown. I'm not asking you to stop altogether... maybe just limit it to a few.
Alcohol dehydrates the body, which can lead to dry and dull skin. It also impairs the absorption of essential nutrients needed for collagen synthesis, such as vitamin C and antioxidants. To keep your collagen intact, opt for moderation if possible.
Smoking is notorious for its detrimental effects on the skin, including collagen degradation. Cigarette smoke contains harmful chemicals that damage collagen fibers and hinder collagen production.
Smoking also restricts blood flow to the skin, depriving it of oxygen and nutrients necessary for collagen synthesis. Quitting smoking can significantly improve collagen preservation and contribute to healthier, more vibrant skin.
By reducing alcohol consumption and quitting smoking, you create a healthier environment for collagen synthesis and minimize collagen damage. This, in turn, can help maintain skin elasticity, firmness and a more youthful appearance.
How much collagen do I need to take for skin?
The optimal amount of collagen to take for skin health can vary depending on factors such as individual needs, age and overall health.
While there is no specific daily recommended intake for collagen, studies and anecdotal evidence suggest that a range of 2.5 to 10 grams of collagen peptides per day can provide potential benefits for skin.
It's important to note that collagen supplementation works in a cumulative manner, meaning that consistent daily intake over a period of time is more impactful than sporadic or inconsistent consumption. The body needs a sustained supply of collagen peptides to support collagen synthesis and maintenance in the skin.
When selecting a collagen supplement, pay attention to the dosage instructions provided by the manufacturer. They will often recommend a specific serving size or number of capsules/tablets to take daily.
I'll say that sometimes they are artificially inflated to get you to use more of it faster. A good starting point is 10 grams per day.
What type of collagen is best for loose skin?
When it comes to loose skin, type I collagen is generally considered the most beneficial. Why is this the case? Type I collagen is the most abundant collagen in the human body and plays a significant role in skin structure and elasticity.
It provides strength and support to the skin, helping to maintain its firmness and reduce sagging.
While type I collagen is the primary collagen in the skin, it's important to note that collagen supplements typically contain a combination of different collagen types, including type I, II, III and others.
Sure, below is a concise table detailing the five most common types of collagen and their primary uses, based on the provided research:
|
Collagen Type |
Description |
Primary Uses |
|
Type I |
This is the most predominant type of collagen in the body, formed with densely packed fibres. |
It gives structure to skin, bones, tendons, connective tissues, teeth, and fibrous cartilage. It is considered the most beneficial for skin health. |
|
Type II |
Made up of loosely packed fibres, mainly found in the cartilage. |
Its primary function is to provide cushioning for joints. |
|
Type III |
A structural support component present in organs, muscles and arteries. |
It assists in maintaining the structure of organs, supports muscles, and contributes to the health of arteries. |
|
Type IV |
This type of collagen is primarily found in the layers of the skin. |
It aids in filtration and contributes to skin health. |
|
Type V |
It's lesser common than the previous four, finding its presence in placenta, hair, and other specific cell surfaces. |
The primary uses include supporting the health of the placenta, aiding in maintaining hair health, and contributing to certain occular functions. |
These different types of collagen have unique properties and benefits. If you choose a diet rich in foods high in collagen, you’ll receive a wide range of collagen types, all of which have different benefits for your body and skin.
However, when choosing a collagen supplement for loose skin, look for products that specifically mention containing type I collagen. This ensures that you are targeting the collagen type most closely associated with skin health and elasticity.
What vitamins help with collagen production?
Several vitamins play a crucial role in collagen production and support. Incorporating these vitamins into your diet supercharges the benefits of collagen synthesis and maintains healthy skin. Here are some key vitamins that are known to support collagen production:
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a vital nutrient for collagen synthesis. It is involved in the conversion of proline and lysine into collagen fibers. Also, it acts as an antioxidant, protecting existing collagen from damage. Citrus fruits, berries, kiwi, peppers, broccoli and leafy greens are excellent sources of vitamin C.
- Vitamin A: Vitamin A is essential for the formation of new collagen. It helps regulate the production of collagen and supports the overall health of skin cells. Foods rich in vitamin A include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale and liver.
- Vitamin E: Vitamin E is an antioxidant that helps protect collagen from oxidative stress and damage. It also aids in the maintenance of healthy skin cells. Nuts, seeds, spinach and avocados are good sources of vitamin E.
- Biotin: Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, supports the production of keratin, a protein that is vital for healthy skin, hair and nails. It indirectly supports collagen production by promoting overall skin health. Eggs, nuts, seeds and sweet potatoes are good sources of biotin.
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin): Vitamin B3 plays a role in the metabolism of energy and nutrients required for collagen synthesis. It also helps improve skin barrier function and moisture retention. Chicken, turkey, fish, peanuts and mushrooms are sources of vitamin B3.
- Vitamin B6: Vitamin B6 is involved in collagen synthesis and helps convert amino acids into collagen building blocks. Incorporate foods like fish, poultry and beef for you B6.
Are there any side effects to taking collagen supplements?
Collagen supplements are generally considered safe for most people when taken as directed. However, there are times when collagen is bad for you.
It's important to note that individual responses can vary and some people may experience certain side effects or interactions. Here are a few considerations regarding potential side effects of collagen supplements:
Allergic Reactions
While rare, some individuals may be allergic to collagen or have sensitivities to the sources from which it is derived. If you have a known allergy to specific animal sources like fish or shellfish, it's important to choose collagen supplements derived from other sources.
Digestive Issues
Usually, collagen is helpful with digestion. That’s one of the reasons so many people take collagen when they’re pregnant. However, some individuals may experience digestive symptoms such as bloating, gas or an upset stomach when taking collagen supplements.
These symptoms are typically mild and temporary. If you experience any discomfort, it may be helpful to adjust the dosage, take the supplement with food or switch to a different brand or formulation.
Interactions with Medications
Collagen supplements, particularly those sourced from marine animals, may contain high levels of calcium. If you are taking medications that interact with calcium, such as certain antibiotics or medications for osteoporosis, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting collagen supplementation.
Weight Gain
Collagen supplements are generally low in calories and do not contribute significantly to weight gain. However, if collagen supplements are taken in the form of sugary or high-calorie drinks or if overall calorie intake is not considered, it could contribute to weight gain indirectly.
As with any supplement, it's important to follow the recommended dosage provided by the manufacturer and to choose high-quality products from reputable brands like the ones linked in my guide above.
If you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking any medications, it's always wise to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new dietary supplement, including collagen.
Closing Thoughts
If you're looking for a way to improve the appearance of your skin, collagen may be a good option for you. Collagen supplements can help to increase skin elasticity and reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
Be sure to read my guide to collagen supplements for sagging skin so you can choose the right product for your needs.
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8824545/
- https://parjournal.net/article/view/3863
- https://ajp.amjpathol.org/article/S0002-9440(10)62205-5/fulltext
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32520042/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29184426/












Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.