
Collagen for Pregnancy: Is it Safe and What are the Risks?
Collagen for Pregnancy
Nothing is more important to an expecting mom than the health of her growing baby. Of course, moms often have to be reminded that to take care of their little one, they must also take care of themselves.
A collagen pregnancy supplement is one way that many moms-to-be are helping their babies grow strong while improving their own health during pregnancy as well.
Collagen is found throughout the body, from the skin to bones to joints. It is also a vital component in connective tissues supporting a developing fetus.
Here are some of the many collagen benefits during pregnancy for fetus and mother.

Is it safe to take collagen during pregnancy?
Collagen supplements are generally considered safe for consumption, but pregnant women have specific nutritional requirements so its best to double check with your healthcare provider before taking any supplements.
Some collagen supplements may contain other ingredients that may not be safe during pregnancy. For example, some have herbs or extracts that are contraindicated during pregnancy. Therefore, make sure you get a pure product when shopping for collagen supplements.
8 Collagen Benefits During Pregnancy
Collagen benefits during pregnancy include:
- Gut health for hormones
- Pre natal nutrition
- High protein
- Joint support for you and your developing baby
- Placenta and womb health
- Eases morning sickness
- May reduce stretch marks
- Nutrients for a developing baby
Let's go through each of these in a bit more detail.
1. Healthy Gut to Support Your Hormones
Collagen is a crucial component of the digestive system, where it helps to maintain gut health and function. That is because it is full of rare amino acids which are essential for the formation of the gut lining.
You need a healthy gut linking to protect the digestive tract from harmful substances and to support the immune system, which may be weakened during pregnancy.
When pregnant, your digestive system is particularly sensitive. Getting more of this protein may improve gut health by increasing the production of beneficial gut bacteria and laying down new connective tissue to support digestion.
2. Full of Pre-Natal Nutrients
- Glycine: This amino acid that plays a crucial role in fetal growth and development. Glycine is also known to improve the quality of sleep, which can be beneficial for pregnant women who often struggle with sleep issues.
- Proline: This amino acid found in collagen helps in the formation of fascia. It enables the baby’s skeleton, connective tissues, and joints to grow well.
- Glucosamine: This sugar molecule found in collagen helps to maintain joint health and mobility during pregnancy. As the body undergoes various changes during pregnancy, joint pain and stiffness can become common issues, and glucosamine can help to alleviate these symptoms.
- Glutamine: This amino acid is known to support healthy gut function. This can be especially beneficial for pregnant women, as a healthy gut regulates hormone levels.
- Calcium: A mineral essential for fetal development and the formation of strong bones and teeth, calcium is also important for maintaining healthy muscle and nerve function.
3. Protein if / When You Can't Stomach Meat
My wife just gave birth to our baby boy. Throughout the first and 3rd trimester her tastebuds changed drastically. She no longer craved meat or sugar... oddly enough.
One thing that was a lifesaver for her was a high protein bone broth.

Many women may struggle to eat enough meat or other high protein food due to nausea, aversions, or dietary restrictions. This is where collagen can be beneficial.
It has all of the essential amino acids that the body needs to function properly. One of the best benefits s is that it increases protein intake without you (or the mom) having to eat meat.
You can easily add it to smoothies, soups or baked goods to increase protein content without upsetting delicate tummies.
4. Support for You and Your Babies Joints
As the baby grows, it places stress on the mother's joints, which can lead to discomfort and pain or even injury. Collagen is a primary component of the cartilage that cushions our joints.
Some studies show that they can improve joint function and reduce chronic pain.
Collagen also supports the development of the baby's joints since it’s a crucial building block for the formation of bones, cartilage, and other connective tissues.
5. The Health of the Womb Lining and Placenta
Your placenta is made just for your baby. It is responsible for providing essential nutrients and oxygen to the growing fetus, so a healthy placenta is crucial for a healthy pregnancy.
Collagen contains amino acids which are important building blocks for the formation and maintenance of the placenta and womb lining.
This is why it’s wise to get plenty of collagen rich foods even extremely early in the pregnancy, when the placenta is still growing.
6. Gets Rid of Morning Sickness
While collagen has not been shown to directly cure morning sickness, it can indirectly help alleviate some of the symptoms.
One of the main causes of morning sickness is stomach acid going up into the throat, which can lead to nausea and vomiting.
Glycine (found in bone broth and collagen) is an amino acid that helps regulate stomach acid production and promotes a healthy digestive system.
Glycine also stabilizes blood sugar levels, alleviating morning sickness symptoms.
7. May Reduce Stretch marks
Collagen provides strength and elasticity to the skin's structure. After all, that’s why it’s so popular in skincare. You might notice that it reduces the appearance of stretch marks because of how it hydrates and nourishes your skin.
8. Nutrients for Baby Development
Collagen is full of building blocks that your baby needs to thrive and develop properly. Here's a few of the key players and what they do:
- Glycine helps to build and repair tissues and is especially important for the development of the fetal brain and nervous system.
- Proline is important for tissue formation and wound healing as well.
- Glucosamine is crucial for the development of healthy joints and cartilage.
- Calcium helps your baby develop strong bones and teeth.
What are the risks associated with using collagen supplements during pregnancy?
The risks with collagen during pregnancy are that it may not work for you, some people have allergic reactions or get nauseous and there are huge sourcing and quality concerns.
I'll outline each of these below for you.

1. No direct research on pregnant people
There is limited research on using collagen supplements during pregnancy. That does not mean it doesn't work, just that it has not been studied formally. While collagen is generally considered safe, it’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements or vitamins.
2. It does not work for everyone
Pregnant women respond differently to different thing. Every pregnant women knows how a certain food can be the most appealing thing one day and revolting the next. Collagen is no exception. It may soothe your stomach one week and seem to irritate it the next.
3. Potential for digestive issues and allergic reactions
It can be difficult for some people to digest collagen protein, especially if they have a history of struggling to digest protein or a sensitive stomach.
Also, these products are made from animal sources such as cow, chicken or fish, which some women may be allergic to. Check the source carefully if you have allergies.
4. Sourcing and quality issues
For the most part, collagen peptides come from large industrial feedlot farms. The quality varies depending on factors such as the animal's diet and how the amino acids are extracted and processed.
If the collagen is sourced from animals that were given antibiotics, hormones or other chemicals, those substances could potentially be passed on in the collagen.
Collagen that isn’t extracted and processed properly can be contaminated with harmful substances, like heavy metals.
To mitigate these risks choose high-quality, reputable brands which are clear about their sourcing, extracting and processing procedures.
Some products may contain other ingredients. Vitamins like Vitamin C or D are important in the right doses, but you don’t want to accidentally take too much.
How to take Collagen Peptides During Pregnancy
- Talk to your doctor to make sure they’re on board with pregnancy collagen
- Choose your format (powder, pills or bone broth)
- Start with 5-10 g per day
- Measure how you look and feel after 2-3 weeks and adjust your dose
How can you incorporate collagen into your diet during pregnancy?
1. Eat Collagen Rich Foods
Here are a few collagen rich foods to get you started:
- Gelatin, derived from collagen, can be mixed into jello, soup or ice cream.
- Pork rinds, made from fried pork skin, are a low-carb snack with up to 10 grams.
- Fish such as salmon, sardines, mackerel, herring, and anchovies are rich in collagen, but buy and consume them with skin and bones intact.
- Chicken skin, pork spare ribs, beef short ribs, and oxtail contain significant amounts of it and are often used in stews and soups.
- Chicken wings are also a tasty collagen-rich snack.
- Shellfish such as clams, mussels, and oysters contain limited amounts of collagen, but pregnant women should be careful about consuming them and never have them raw.

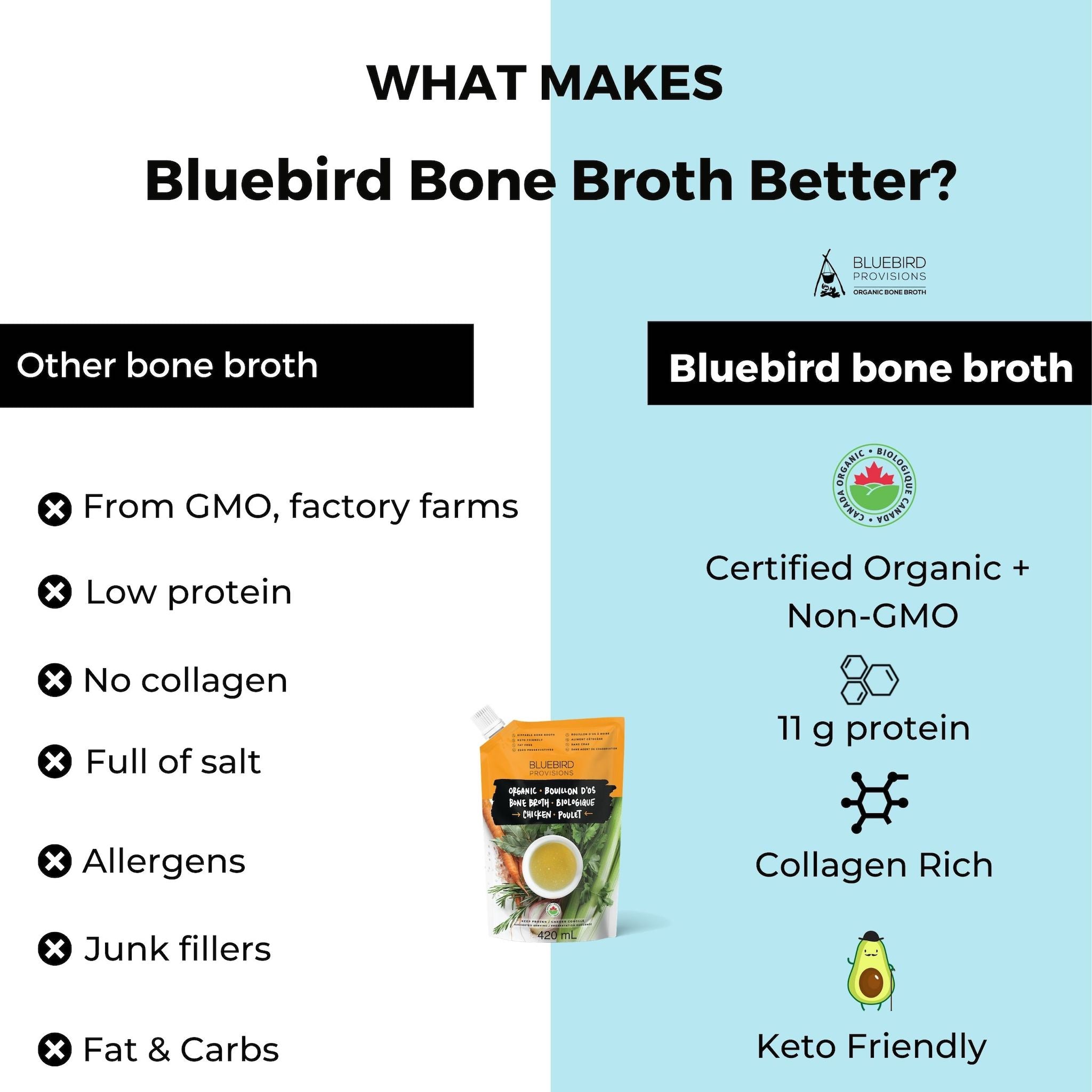
2. Drink bone broth
Bone broth is one of the simplest and most delicious ways to get your daily dose. Bluebird Provisions bone broth is nourishing and easy on the stomach.
Bone broth powder is easily digestible and convenient for pregnant moms who never have enough time to prepare other high protein meals.
Starting slow, work up to consuming about 10 scoops per week. Incorporate it into your daily routine by drinking it with breakfast, before bed, during meals, before exercise, or when you feel nauseous.
3. Consume gelatinous meats like salmon, shellfish and animal skin.
Canned or whole salmon and shellfish are good sources of collagen because they contain the skin and bones/shell. The skin and bones of salmon are especially rich in collagen.
Make a salmon bone broth or cook the fish with the skin on. Shellfish like oysters and mussels can be added to soups or stews to increase collagen intake.
Animal skin can be roasted or fried to make a crispy snack, or added to soups and stews to enhance the flavor and boost vitamins and minerals.
Looking for a supplement recommendation? Read my guide to finding the best collagen supplement.
How much collagen should you take during pregnancy?
There is no specific recommendation for how much collagen a pregnant woman should take. From a practical perspective, you can start with 10 g per day or else follow the dosage instructions on the packaging. Be sure to consult with a healthcare provider before adding any new supplements to your diet.
What type of collagen is safe to take during pregnancy?
Choose high-quality, reputable brands and consult with a healthcare provider before adding any supplements to your routine during pregnancy. Marine collagen may not be best to take during pregnancy since it may have mercury.
When should I take collagen during pregnancy?
You can take collagen at any time of the day that is convenient for you. However, many women find it more convenient to take it in the morning or before bed so it can ease morning sickness. It can be added to smoothies, beverages, or food.
Can collagen help ease labor pains during pregnancy or postpartum?
Collagen has anti-inflammatory properties which may help reduce inflammation and promote healing after childbirth. Also, it can support joint health, which may be helpful for postpartum recovery.
Closing Thoughts
There are many benefits to taking collagen supplements during pregnancy, but there are also some risks to consider.
Be sure to talk to your doctor before taking anything, and only purchase from a trusted source. Bluebird Provisions bone broth is a great option for a natural source of collagen with 10 g per cup. You can find them on their website or on Amazon prime.
Disclaimer: this information is for educational purposes only and has not been evaluated by the FDA or CFIA. It is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Please consult your primary care physician for advise on any of this.













Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.