
Gut Brain Connection: How Your Diet Impacts Mental Health & Anxiety
How to Increase Your Gut Brain Connection Through Diet
Have you had butterflies or an urge to use the bathroom when you’re nervous or stressed?
These sensations are evidence of the gut-brain axis.
Here’s a quick story to illustrate how they are connected.
Growing up I raced track and field. I remember my dad taking me to the track for races. He patiently stood with me while I warmed up.
The issue is, before races I am a nervous wreck. I’d visit the bathroom multiple times in the last 15 minutes before any race... expelling my insides.
Even directly after, I’d have butterflies and sensations that I had to urinate. The same sensations replayed before long-car rides. This made for a stressful time getting to summer camp.
In hindsight, maybe my link was too strong.
A quick note before we get started: my company makes and sells irresistibly delicious bone broth made for your digestive health. You can learn more if you like, or continue reading.

What is the gut brain connection?
The gut brain connection is a network of nerves that allows your brain to communicate directly with your gut microbiota. Your gut can also talk to it in return.
This communication network is referred to as the gut-brain axis. Some go so far as to call the gut our second brain.
This is why anger, sadness, happiness, depression and panic can all produce symptoms in your gut (1).
So can the thought of eating. When you’re hungry, your gut begins to release stomach juices to prepare for incoming food.
As I mentioned above, this line goes both ways. When you have gut issues, it can cause anxiety, depression or stress.
Read below to learn how this works. It's fascinating!
How is the digestive system connected to emotions?
Your digestive system is connected to emotions physically through something called the vagus nerve. This nerve is what connects your digestion to your brain.

It is a spindly circuitry of nerves that runs from the back of your brain down to your organs and gut.
It's constant stream of message are responsible for automatic or unconscious bodily processes like controlling your heart rate and digesting food.
It helps connect the 500 million neurons and microorganisms in your gut to the 100 billion neurons in your brain. In case you’re wondering, neurons are cells in your GI tract that have constant interactions with your brain.
Studies show that people with GI disorders like Crohn's Disease or Irritable Bowel Syndrome suffer from a dysfunction or poor responses of their nerve (2).
Also, stress is shown to breakdown its function to cause gut mutation in animals. The vagus nerve is the centrepiece to our emotions.
Having trouble with digestion? Read my guide to instant bloating relief.
The Gut Microbiome Brain Connection
The gut microbiome brain connection is a new theory that there is an intimate relationship between the gut and brain, which can influence cognitive function. It shows that changing your gut bacteria will have an impact on mood, brain and mental health.
To take a step back, over 400 species, 100 trillion microbes and three pounds of bacteria make up your gut. Science people call this system your gut microbiota, which is crucial to your health and longevity.
Your gut microbes help you digest food, regulate hormones, excrete toxins and produce vitamins that directly affect brain function.
Hunger is one way your gut changes your brain. Your gut does this by making short-chain fatty acids from fiber in your diet. These fatty acids reduce appetite.
Some studies show that consuming these fatty acids can reduce your desire for food (3). This is one reason why people tell you to eat more fiber. That.. and fiber keeps your ‘regular’.
Gut Brain Connection and Mental Health
Our gut brain connection dictates our mental health because many important mood boosting neurotransmitters like serotonin and GABA live in the gut.

Did you know that 95% of your body’s serotonin resides in your gut? That’s because your gut is responsible for producing neurotransmitters (4).
Serotonin changes mood, appetite, alertness and energy and plays a major role in depression.
GABA is another neurotransmitter crucial to positive moods. Our gut bacteria need GABA to thrive.
At this point you may be asking: what is GABA?
GABA calms us down. It helps regulate mood and depression. And a lack of GABA could lead to depression. It’s incredibly important to your mental health.
What I find interesting is that GABA is being used to restore gut bacteria to treat depression in human and mice models (5).
Ok, so now we know that a healthy gut means a happy life. How do we know if our gut isn’t healthy?
What are some of the benefits of having a healthy gut brain connection?
The benefits of having a healthy gut brain connection are crucial to your long-term health, they are:
- Reduced inflammation
- Proper digestion as the cornerstone of all health
- Decreased depression and anxiety risks
- Decreased risk of Alzheimers, Parkinson's and dementia
Inflammation, Gut health, Depression and Dementia
A strong gut axis is crucial for a resilient immune system and warding off chronic health issues like depression and dementia or neurodegenerative disease.
Your gut bacteria is responsible for controlling inflammation. There is a mucosal lining in your gut. This lining is like a doorman in a nightclub.
Your gut lining controls which food particles go into your bloodstream and which get denied.... (and go home early... sounds like me in university).
Bad food, stress and pollution all cause wear and tear on your gut lining, making it porous.
This is referred to as Leaky Gut Syndrome.

It’s like the bouncer left and everyone can get into the club. Chaos.
The problem is that your immune system gets activated when particles start leaking through your gut lining.
If you have a leaky gut, then your immune system is constantly activated, leading to inflammation.
This inflammation creates harmful toxins in your gut bacteria, which have free access to your bloodstream if your gut is leaky.
Inflammation causes many disorders like Alzheimer’s, depression and schizophrenia (6). We first saw this is mice, but now there's a host of human research cases to support it.
Of note for you and me, inflammation is implicated in just about every other chronic disease, including heart disease, diabetes and autoimmune conditions.
Gut Brain Connection Anxiety
Anxiety impacts the gut brain connection by sending singles down the vagus nerve into the gut. This messes with the balance of your gut flora, making you feel awful and ill.
Stress also directly affects movements and contractions in your gut and GI (gastrointestinal) tract.
Given the systems are interlinked, it makes sense that you get butterflies before a presentation. Or in my case, have to go to the bathroom before races.
Your gut works with your psychology to influence these movements.
Interestingly, people with GI conditions like crohn’s or colitis are more sensitive to pain. This is because their systems are hyper-aware of all signals coming from their gut.
In other words, stress can make your pain feel worse.
The good news is that you can treat GI conditions and improve your well being by using techniques for anxiety and depression.
The gut brain axis can help us rebuild our GI tract. It starts with managing your stress.
Can probiotics help your gut brain connection?
Probiotic have a protective effect on your gut. We know that gut bacteria affects brain health. How do probiotics fit into the equation and what are psychobiotics? Read below, my friend.
Probiotics are good bacteria already living in your large intestine. They feed on prebiotics to flourish and grow.
Prebiotics, the less known cousin, are soluble fibers that feed good bacteria in your gut. The cool thing is that they reduce the nasty stress hormone: cortisol.
Some common sources:
- Onions
- Leeks
- Asparagus
- Artichoke hearts
- Garlic
- Chicory root
Probiotic foods that can complement your existing bacteria include:
- Sauerkraut
- Yogurt
- Pickled foods
- Kefir
- Kimchi
- Kombucha
Read your labels carefully. You want to avoid buying anything with added sugar or preservatives.
Yogurt in particular is full of sugar. Opt for full fat yogurt that is plain or unsweetened. You can add your own sweetener like maple syrup, cinnamon or berries.
Psychobiotics: The New Probiotic

There is a new class of probiotics referred to as psychobiotics which are specifically used to optimize the gut-brain axis.
Early research suggests that psychobiotics can help to treat depression, chronic fatigue syndrome and GI disorders like IBS (7).
Other studies use different psychobiotics to treat stress, anxiety and depression. In other words, food is medicine. Food can directly improve your mood. How cool is that?
The specific strain of psychobiotic used is Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 taken for 6 weeks.
What foods contain Psychobiotics?
The best foods that contain psychobiotics are dark, leafy green vegetables, goat dairy products, like yogurt, kefir, seaweed and miso soup
Foods to Strengthen Your Gut Brain Axis
The best foods to strengthen your gut brain axis are fatty fish, bone broth, mushrooms, kefir, asparagus, sesame seeds and coffee.
Now, I realize that you probably skipped the whole article to get this food list. Scroll down for a detailed explanation.
Before you add things, make sure you should avoid inflammatory foods or else your efforts will be useless. This is referred to as 'via negativa' in Latin, meaning that it's easier to remove things than it is to add them.
My point is that you should also avoid processed foods as they kill your gut bacteria.
Gut Brain Connection Diet
The Mediterranean Diet is a great starting point to optimize your gut brain axis. It’s shown to be protective against depression (8).
The Mediterranean Diet focuses on whole grains, seafood and poultry, beans, legumes, fruit and vegetables (leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables) along with nuts and olive oil for cooking.
If we dig a little deeper, we can find more specific foods for your gut-brain axis.

Omega-3 Fats
Omega-3s are found in oily fish and algae. They are also highly concentrated in your brain. Omega-3s help reduce the dangerous inflammation that is responsible for many chronic diseases.
Omega-3s boost your brain health and can lower your risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s (9). They also build a healthy gut in mice and humans.
Probiotic Rich Foods
As I mentioned above, probiotic rich foods nourish your gut with good bacteria so it can thrive.
A healthy gut-brain axis protects your immune system and keeps you healthy.
Kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, yogurt and kombucha are all great natural sources of probiotics.
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are a soluble fiber that your gut bacteria feeds on. They reduce stress hormones and help your gut function properly.
Natural sources include: asparagus, artichoke hearts, leeks, onions and garlic.
Mushrooms
Shiitake mushrooms are naturally high in vitamin B-6. B-6 is crucial to the production of serotonin in your gut.
90% of the serotonin is made in your gut. It then travels up your vagus nerve to your brain.
Polyphenols
Polyphenols are plant compounds that improve your brain health, memory and healthy gut bacteria. They’re important to your autonomic nervous system.
Polyphenols are found in green tea, coffee, cocoa and olive oil.
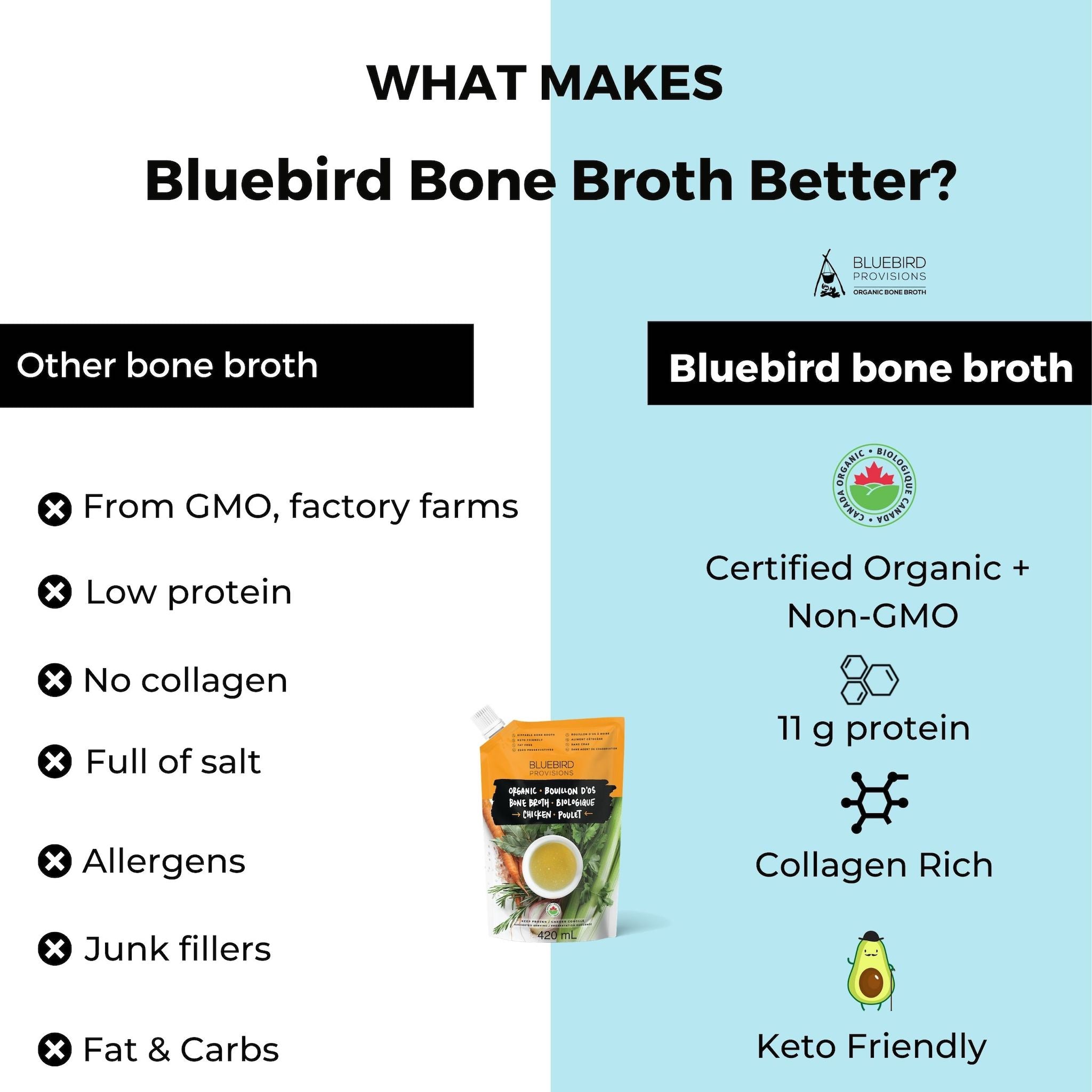
Bone Broth
Bone broth is full of an amino acid called glycine. Glycine improves your mood, memory and cognition because it helps with brain signalling.
It also helps your digestion by decreasing inflammation and healing damaged tissues in your intestines.
One cup of Bluebird Provisions bone broth has the 3 g needed for digestive health benefits.
Sesame Seeds
Sesame seeds are rich in tyrosine, an amino acid that increases dopamine in your brain. Dopamine helps you feel motivated, and is important to this system.
How do you heal a gut brain connection?
There are four reliable ways to heal a gut brain connection. These treatment methods include:
- Relaxation therapy. This approach offers specific behavioral strategies to help people relax and reduce their anxiety.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy
- Gut-directed relaxation training
- Biofeedback
Closing Thoughts
Your gut and your brain are physically and chemically connected through your vagus nerve. And because of this, many of the crucial neurotransmitters like serotonin are made first in your gut.
You can improve your brain health, reduce stress and anxiety by changing your gut bacteria.
There are many foods you can eat to boost your gut-brain axis, these include: omega-3s, probiotics, bone broth, polyphenols, mushrooms and sesame seeds.
The easiest way to get started is to drink one cup of bone broth per day. Bluebird Provisions Instant Chicken Bone Broth is delicious and has all the gut healing nutrients you need to feel better.
Do you get butterflies or feel sick when you’re stressed? Leave a comment and let me know.
Some extra FAQs are posted below.
Is gut health linked to anxiety?
Gut health is directly linked to anxiety because of the vagus nerve. In fact, one of the most common side effects of stress and anxiety is stomach problems, which is often caused by your enteric nervous system. These nerves are interconnected with your brain like a second brain.
How can you improve your gut brain connection?
You can improve your gut brain connection by focusing on your digestive system first. Follow these steps:
- Remove foods that disrupt your digestion or do not agree with you.
- Try gut and brain healing foods like bone broth, probiotic foods, omega-3s and more.
- Practice mindfulness, relaxation therapy or cognitive behavioural therapy.
- Look into gut directed biofeedback training.
- Consider hypnotherapy
How can I stop my gut brain connection anxiety?
You can stop your gut brain anxiety by trying these tips:
- Keep a food diary to figure out which foods that cause you digestive issues or make you feel bad.
- Learn which foods boost digestion and brain health like bone broth, kefir, fatty fish and short chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
- Consider cognitive behavioral therapy, meditation or biofeedback gut training. Studies show that practicing mindfulness can help reduce anxiety and playing music has been shown to stimulate creativity in the brain.















2 comments
I consume sesame oil, probiotics, tofu, kefir, natto, avocadoes, green tea on a daily basis. I just love those foods and actually never knew the gut/brain benefit.
Love this information..
P. Turner
Need to find book about this subject and how to prepare foods to maintain nutrients. I am a senior in my eighties constant butterflies. Bit of brain fog memory really good for traveling. Short term memory need to follow through not say I will look that up after.
Roger Rolfe
Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.