
Natural Collagen Sources: 9 Foods That Contain This Healthy Protein
Natural Collagen Sources
For years, I had struggled with joint pain and stiffness due to a sports injury I sustained in my twenties.
None of the various supplements and medications seemed to provide long-term relief without annoying side effects. Then I stumbled upon the benefits of collagen.
I thought I’d been getting enough from my high-meat diet, but I was wrong. It took a bone broth supplement to get me the relief I was looking for.
This got me wondering, what are the natural collagen sources, and how much do you need to consume?
The spoiler is that the best natural source if a high protein bone broth. My favorite for this is made by a small company called Bluebird Provisions.
They make a delicious chicken bone broth and a beef one for dogs.
Why do You Need Collagen?
We all need collagen to boost our own internal production in order to keep wrinkles at bay, fix achy joints, preserve muscle mass and connective tissue.
Why is that? For starters, collagen is the most abundant protein in our body. It makes up our connective tissue, including skin, bones, muscles, tendons and cartilage.
Collagen production naturally decreases with age (unless you use these boosting strategies). However, lifestyle factors can speed up the process.
Excessive alcohol use, smoking, sun exposure and nutrition deficiencies are notorious killers of this protein.
The result is not only visible effects like wrinkles, but also weakened muscles, tendons, and ligaments, resulting in joint pain and osteoarthritis.
Supplements can benefit collagen production, but it's essential to know the facts before adding them to your daily routine.
|
FOODS HIGH IN COLLAGEN PROTEIN |
|||
|
FOOD |
COLLAGEN PER SERVING |
SERVING SIZE |
NOTES |
|
BONE BROTH |
8-10 G |
1 CUP |
MUST HAVE 10-12 TOTAL PROTEIN PER 250 ML. |
|
GELATIN |
10 G |
10 G |
|
|
PORK RINDS |
10 G |
28 G |
DEEP FRIED PORK SKIN. |
|
SALMON |
6.5 G |
170 G |
COOKED SOCKEYE SALMONE IN OVEN (1 filet). |
|
PORK SKIN |
5 G |
14 G |
HERRING, MACKEREL IN A CAN WITH SKIN + BONES. |
|
SARDINES |
5 G |
150 G |
HERRING, MACKEREL IN A CAN WITH SKIN + BONES. |
|
CHICKEN SKIN |
4 G |
14 G |
|
|
PORK SPARE RIB |
3.5 G |
85 G |
MUST BE SLOWED BRAISED. |
|
BEEF SHORT RIB |
3 G |
85 G |
MUST BE SLOWED BRAISED. |
|
BEEF OXTAIL |
2.5 G |
75 G |
|
|
CHICKEN WINGS |
2.5 G |
105 G |
WING MEAT AND SKIN ( 1 wing). |
How to Increase Collagen Through Your Diet
The best way to increase collagen through your diet is to add collagen-rich food sources. Foods like bone broth, fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, cod, herring and mackerel, as well as gelatinous meats are all full of these crucial amino acids.
It's also important to prioritize sleep, as growth hormones activated during sleep can stimulate collagen production.
Lastly, foods that are rich in Vitamin C, A and copper provide the building blocks for collagen building in your body. can help increase collagen production, as can snacking on nuts.
9 Natural Collagen Sources
The top 8 natural collagen sources are bone broth, skin, small fish (you'll never guess why), pork rinds, beef roasts, shanks, short ribs and chicken drumsticks.
Let's go through each and I'll tell you how to maximize them in cooking.
1. Bone Broth
Animal bones, fish bones, connective tissue and marrow are rich in important minerals, vitamins and compounds. This is what makes up any quality bone broth.
You also get a great balance of calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus and gelatin.
These nutrients are released into the water when simmered and can be easily absorbed by the body.
However, the exact nutrition in the broth may vary depending on the batch of bones used, the brand and the cooking technique.
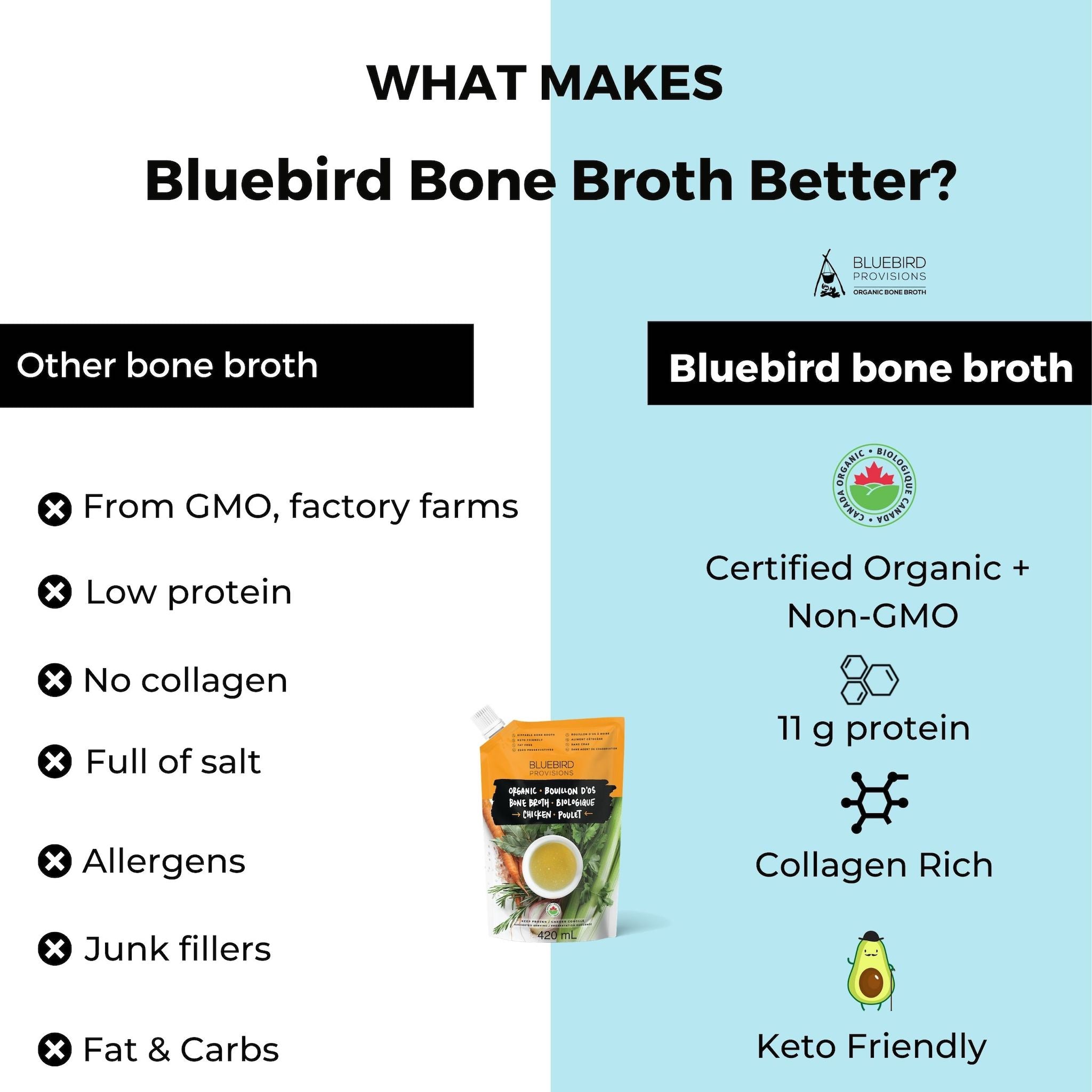
If you're looking for a convenient, whole food source of collagen protein, Bluebird Provisions Chicken bone broth powder is a great choice with 10 grams per cup.

Unlike other products that may contain gums, fillers, or 'natural flavors,' Bluebird Provisions has developed a powdered bone broth that is easily digestible and tastes like real chicken bone broth.
In addition to being a convenient source of collagen protein, bone broth also has hydrating electrolytes which can help you stay hydrated while supporting healthy skin, joints, and bones.
Plus, it's a great way to build a healthy gut thanks to its amino acids like glycine, proline and glucosamine, which can improve digestion and decrease inflammation.
I drink 4-5 cups of bone broth per week and I regularly get comments on my skin despite (embarrassingly) not washing my face or using any type of skincare products.
2. Animal Skin (chicken, fish, pork)
Animal skin is a good source of collagen because collagen is the main structural protein found in animal connective tissues, including skin.
Skin is a common source of commercial collagen extraction (1), but it’s also good for collagen when prepared at home.
When animal skin is boiled or cooked, the collagen fibers in the skin break down and release collagen protein.
Animal skin is a particularly rich source because it contains high concentrations of type I collagen, which is the most abundant type of collagen in the human body (2) and is responsible for providing strength and support to the skin, bones, and other tissues.
From a practical perspective, I would urge you to eat the skin on the meat you consume. You can easily do this with chicken, pork and fish. It really is nature's multivitamin.
3. Sardines, Anchovies, Herring
Sardines, anchovies, and herring are all types of small, oily fish that contain a significant amount of collagen because you can eat the whole skeleton with the meat.
You read that correctly. The canned fish you find in the store often has the full fish skeleton and skin along with the flesh.
The way they are processed, the bones are soft and edible. These are a goldmine for crucial collagen building amino acids with around 6 grams per serving.

This fish collagen is highly bioavailable, meaning that it is easily digested and absorbed by the body.
In addition to collagen, sardines, anchovies, and herring are also rich in other important nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, that are essential for maintaining healthy skin, bones and joints.
As an added benefit, these fish are relatively healthy and affordable making them a great choice for people who want to boost their collagen intake without breaking the bank, harming the environment or gaining weight.
4. Pork Rinds
Pork rinds, also known as chicharrones, are a fried snack made from pork skin. Pork skin not only cheap and delicious, but also rich in collagen with up to 15 grams per serving.
When pork rinds are fried, the heat breaks down the protein in the skin, making it easier for the body to absorb.
Pork rinds are a low-carb snack, which makes them a popular choice for people on a low-carbohydrate or ketogenic diet. With a 1-ounce serving containing around 17 grams of protein, pork rinds are also a good source of protein (3).
Keep in mind that pork rinds are high in fat and sodium, so they should be consumed in moderation.
5. Salmon
Like many other marine collagen sources, salmon is incredibly well absorbed. When cooked, the heat breaks down the glycine and proline in the skin, making it more accessible for the body to digest.
Plus, salmon skin is absolutely delicious.
Salmon is also a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties that can help improve skin health and reduce the signs of aging.
The vitamin D and astaxanthin in salmon can protect the skin from sun damage and improve skin elasticity.
6. Pork Ribs
Pork ribs contain connective tissue, cartilage and tendons that is rich in collagen. When cooked for an extended period of time, the heat breaks down the collagen in the connective tissue,
This makes it easier for our bodies to digest and absorb the protein where we need it most. Like out knees, hips and tendons.
The byproduct of this slow cook is an absolutely delicious rack of ribs!
Whether slow-cooking, smoking, or grilling, enjoy different flavors and textures while your body reaps the reward of eating collagen-rich connective tissue.
Pork ribs are also a good source of protein, with a 3-ounce serving containing around 22 grams of protein.
7. Beef Roast
Like pork ribs, beef roast contains bioavailable connective tissue, such as tendons and ligaments, that are full of collagen. Beef roast is also a good source of protein, with a 3-ounce serving containing around 25 grams of protein.
Maybe you're surprised by this one on the list? Let me explain.
When cooked slowly, the heat breaks down the collagen in the connective tissue, making it more accessible for the body to absorb.

Also, The broth produced from the trimmings and extras of beef roast is also a great source of collagen.
Slow cooked, roasted, or braised, beef roast can be cooked in a variety of ways while still maintaining the collagen-rich connective tissue.
In addition to collagen and protein, beef roast also contains other beneficial nutrients like:
- Iron
- Zinc
- B vitamins
8. Short Ribs
Short ribs are a good source of collagen because they come from a heavily exercised muscle area of the cow, which contains a lot of connective tissue and collagen.
The collagen in short ribs breaks down during the cooking process, resulting in a tender and flavorful meat.
Additionally, cooking methods that involve moist heat, such as braising or stewing, can further break down the collagen and make it even more easily digestible.
9. Chicken Drumsticks
Chicken drumsticks are a good source of collagen because they contain a lot of connective tissue, particularly in the skin, tendons, and cartilage.
These connective tissues break down during cooking and provide a rich and flavorful broth when cooked in liquid or crispy snack when fried or baked.
What vitamins and minerals are important for collagen production?
Vitamin C, Vitamin A, copper, zinc and manganese are the vitamins and minerals crucial to collagen production.
- Vitamin C helps to shuttle amino acids into your joints, tendons, skin and ligaments.
- Zinc, a cofactor that contributes to the function of the enzyme collagenase, which breaks down and turns over outworn or injured tissues.
- Vitamin A protects collagen from breakdown and enhances the production of new proteins.
- Copper, which works with the enzyme lysyl oxidase to cross-link collagen and assist in "weaving" together fibrous connective tissues
- Manganese plays a role in the creation of proline. Without these cofactors, collagen supplementation may not be used appropriately by the body.
Can you get enough collagen from real food?
You can get enough collagen from real food provided that you eat the right foods in the right quantities and drink bone broth.
As someone who enjoys meat in their diet, I thought I was getting enough collagen from the connective tissues found in chicken, beef and pork.
However, as I learned more about the importance of collagen for overall health, I realized that I wasn't eating enough of these connective tissues to make a significant impact.
I learned that while it's possible to get some collagen from real food sources like chicken, beef, fish, and pork, it can be challenging to consume enough collagen through diet alone.
That's because many of us don't eat enough of the connective tissues that contain collagen, such as bones, skin, and tendons.
To increase your collagen intake, first think about eating nose to tail. This includes skin, organs, connective tissue, fat, gristle and bone broth.
Do you really need a collagen supplement?
Collagen supplements provide a concentrated source of collagen, making it easier to meet daily collagen requirements, particularly for individuals who may not consume enough animal-based protein sources.

Collagen supplements can also be useful if you have specific health concerns related to collagen, such as joint pain or skin aging.
Looking for a supplement recommendation? Read my guide to finding the best collagen powder.
For example, my wife just gave birth to our baby boy. She is drinking bone broth but struggles to get more than one cup per day.
In this case, I got her some peptides to help increase her daily intake.
Are there any risks associated with eating collagen-rich foods?
Taking too much collagen supplements can be harmful as it can throw off the balance of amino acids in your body and lead to adverse side effects such as headaches, digestive issues and fatigue (4).
Some people may also be allergic or intolerant to collagen. It is recommended to speak to a doctor before taking collagen supplements, especially if you have any preexisting medical conditions or are taking any medications.
How do certain foods increase collagen levels?
Gelatinous meats, ribs and tough cuts of meat are full of the amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline which are important for collagen production.
Nutrients such as zinc found in shellfish, nuts, and beef as well as vitamin C found in citrus fruits, berries, leafy greens, bell peppers, and tomatoes are also required for collagen production (5).
Nutrients that Boost Collagen Production
Vitamin C
Vitamin C helps move amino acids into our skin and cells. This works to create and link together these amino acids into collagen strands.
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps to protect collagen from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Additionally, vitamin C helps to activate enzymes that are involved in the process of collagen synthesis.
To ensure the efficient absorption of collagen into your tendons and ligaments, it is advisable to consume collagen-containing foods or supplements before or with a meal that contains vitamin C.
However, for optimal collagen production in tendons, I recommend taking collagen along with 50 mg of vitamin C one hour prior to weight training or exercise.
Vitamin A Rich Foods
Vitamin A plays a crucial role in the production of collagen because it helps to regulate the growth and differentiation of cells that make up the skin, bones and other tissues.
Vitamin A helps to promote the production of new collagen by stimulating the fibroblasts, the cells responsible for producing collagen in the body.
Also, vitamin A helps to protect collagen from damage caused by free radicals, which can contribute to premature aging and other health issues.
Foods High in Copper
Copper is an essential trace mineral that plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis. It is involved in the cross-linking of collagen fibers, which helps to give the collagen structure and strength.
Copper is also required for the enzyme lysyl oxidase, which is responsible for cross-linking collagen and elastin, another important protein in the skin.
Glycine
Glycine is an amino acid that plays a crucial role in collagen production. Collagen is made up of several different amino acids, including glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline.
Glycine is essential for the formation of collagen, as it is required for the synthesis of proline and hydroxyproline.
In addition to its role in collagen synthesis, glycine also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce inflammation in the body and promote healthy skin, hair, and nails.
Proline
Proline is an important amino acid that helps to stabilize the structure of collagen molecules. It does this by forming strong chemical bonds with other amino acids in the collagen protein chain.
Proline also plays a key role in collagen synthesis, helping to ensure that there are enough building blocks available for the body to produce new collagen.
Closing Thoughts
I hope this guide has inspired you to seek out natural collagen sources to improve your overall health! If you're looking for a delicious and convenient way to get collagen, try Bluebird Provisions bone broth.
It is the only whole food source of collagen that actually gives you more benefits. You can find this brand on Amazon or their website.
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9219788/
- Current Insights into Collagen Type I - PMC (nih.gov)
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/collagen/#:~:text=Several%20high%2Dprotein%20foods%20are,dairy%2C%20legumes%2C%20and%20soy.













Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.