
What Do Collagen Peptides Do? Benefits, Side Effects and Dosage
What Do Collagen Peptides Do
You may feel like you've tried everything to improve your health, but nothing seems to work. Your skin is dry and wrinkled, your joints are painful or you're always bloated and gut issues.
Collagen peptides are a supplement that may help you in a variety of ways, from reducing hair loss and improving skin health to reducing joint pain and improving gut health. But what exactly do they do and how do they work?
In this guide, I'll explain what collagen peptides are, what they do and how to take them safely and effectively.
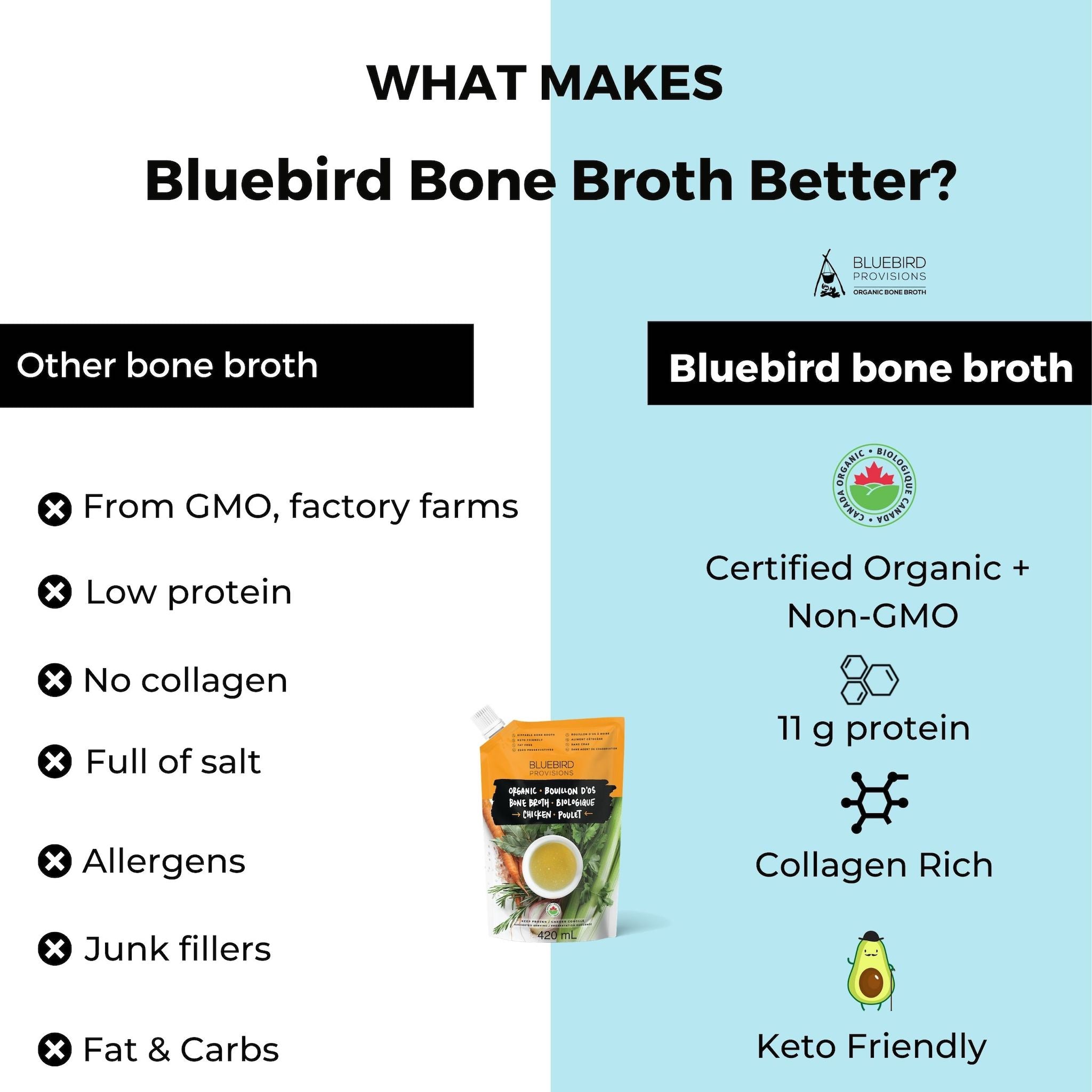
Before we get into that, I'll mention that there is one thing far superior to collagen powder with more benefits and less risk. What is it? A high protein bone broth.
Bone broth has more protein and healing amino acids plus hydrating electrolytes, vitamins and minerals. The most delicious and highest quality one is made by Bluebird Provisions.
First a quick note: this website is reader-supported. I spend a lot of time personally evaluating, testing and reviewing each product on this list. When you buy through links on our site, I may earn an affiliate commission.
What are Collagen Peptides
Collagen peptides are a functional ingredient made from cows, chicken or fish which are used in beauty products, beverages and protein supplements.
The peptides themselves are made by hydrolyzing collagen powder using enzymes to strip out the natural flavor.

This gives you a fine, flavorless powder that mixes readily into hot and cold liquids and does not 'gel' the way gelatin or bone broth does.
They are used to improve skin health, weight loss, joint pain, bloating relief, hair growth and more. Many brands market them as collagen powder and add many flavors to make them taste like chocolate, vanilla or anything else you can think of.
Some of the health benefits have research to support them, while others do not. I will discuss that with you below.
What do Collagen Peptides do
Collagen peptides get broken down into individual amino acids in your body and provide all sorts of health benefits from skin hydration, hair growth, bloating relief, gut health, joint pain and possibly weight loss.
Let's go through a few of them below.
1. May Improve Skin and Hair Health
Collagen peptides are good for skin and hair health, but the research only supports one of these claims. You see, regular use for 8 weeks is shown to reduce wrinkles around the eyes (1).
It also helps to hydrate skin to restore the natural elasticity. How does it work?
Collagen helps to form things called fibroblasts around your dermis layer of skin. Fibroblasts are small clusters of cells. This helps to produce new skin cells which replace the old, wrinkled ones.
If you're looking for a recommendation, read my guide on the best collagen supplement for your skin.
The dosage for skin health is 10 g per day. You can get this from one cup of high protein bone broth.
What about hair growth? Sadly, there is no scientific research that supports the claim that collagen peptides help with hair growth. But many people swear it works, so you can read the article linked above, try it and let me know in the comments if it works for you.
2. Eases Joint Pain
Collagen peptides are shown to help reduce joint pain in people of all ages (2). The study gave participants 10 g collagen over a 24 week period.
The results showed improved markers of joint pain and a decrease in the structural joint deterioration. This means that you can improve your quality of life, ease joint pain and help your body stay healthy and happy as you age.
Researchers think that the amino acids help to repair damaged cartilage and promote connective tissue growth around joints. This reduces inflammation as well.
3. Builds Strong Bones
Collagen is a massive part of our bones. New research shows that taking collagen peptides improved bone mineral density and bone growth markers in women.
The study also showed improvements of blood markers that are associated with bone health. So what is going on here? The amino acids are readily digested into the gut and provide anabolic signals to bones to stimulate an increase in growth and mineral density (3).
The take home point is that if you are at risk of osteoporosis, getting collagen from food will help you. Aim for 5 g daily over a one year period to see results.
I used to get stress fractures from running ultramarathon races. But after I started drinking one cup of bone broth daily (about 10 g collagen), I haven't had one since.

4. May Help With Bloating, Colitis, IBS, IBD and Crohn's Disease
Collagen may help with serious gut issues like IBS or ulcerative colitis thanks to an amino acid called glycine. Glycine makes up about a third of collagen. It is the most potent anti inflammatory amino acid on the planet for your small intestine, large intestine and colon.
You see, our guts get inflamed from stress and eating food we are sensitive to. Unfortunately the list of inflammatory foods is massive. Bad food forms harmful toxins that is able to move outside our gut and into our bloodstream while it is supposed to be being digested.
These toxins pass through tiny holes in your gut that develop from years of bad food and stress. How does glycine fit into the picture?
It lays down new connective tissue in your gut to make sure that no harmful food toxins get into your bloodstream (4).
Nowadays, patients suffering from Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are using glycine as part of the treatment plan (5).
5. Builds Strong Ligaments and Tendons
I used to get sever achilles tendonitis from running. I had it for four years and nothing worked until I found some research about gelatin and vitamin C to heal damaged tendons.
There's an exercise plan described by the scientists about rehabbing ligaments and tendons. It involves taking 15 g gelatin, collagen or bone broth along with 50 mg vitamin C 1 hour before specific exercises.
The exercises must load and target the injured area. In my case, I would use a jumping rope (5 sets of 30 seconds) or do 5 sets of calf raises.
The exercises are crucial because they help to shuttle collagen protein and amino acids into your injured ligaments in order to heal them faster (6).
While this section is relatively brief, you can learn about all of the fascinating health benefits of collagen (including weight loss and blood sugar control) in my dedicated article.
Downside of Collagen Peptides
The downside of collagen peptides are that some people get digestive issues, bloating, allergic reactions, headaches and nausea.
Here are a few things you may be concerned about.
1. May cause digestive issues
While collagen peptides are generally tolerated by most people's guts, some people report bloating, heartburn and water retention.
The hydrolization process is supposed to make it easier to digest, but in my experience, it has the opposite effect for some.
If this is the case for you, I'd recommend trying a high protein bone broth like the one from Bluebird Provisions.
2. May cause allergic reactions
A small percentage of the population are simply allergic to collagen protein. This mean that their gut and immune system will not react well to it.
If this is you, then you'll get a typical allergic reaction to consuming it. If you are sensitive to animal skin or connective tissue, then you may be allergic as well.
3. May cause headaches
Collagen peptides can cause immune reactions to those who can't tolerate some animal proteins, beef or chicken. Also, some people who are histamine intolerant might get headaches when consuming it.
4. Can Cause Kidney Stones
Collagen peptides are rich in an amino acid called hydroxyproline. Research shows that hydroxyproline is converted into oxalates in your body.
Oxalates can get into your urine, which is how kidney stones develop. As long as you are getting normal doses of collagen, there is nothing to worry about.
Learn more surprising side effects in my article on wether collagen is bad for you or not.
Collagen Peptides Dosage
The correct dosage for using collagen peptides is 10 g daily. Most of the research uses 10 g for skin health, joint pain and gut health. Although some research is using 15 g for tendon rehabilitation. Finally, some studies suggest 5 g over a period of 6 months to get joint pain benefits.
Looking for a supplement recommendation? Read my guide to finding the top collagen powder to try today.
There is no need to cycle on and off of it unless you experience allergic reactions. As always, I would recommend that you get your collagen from real food, instead of powders.
What foods contain high amounts of collagen peptides?
Collagen peptide rich foods are bone broth, beef oxtail, small fish, pork rinds, chicken feet, chicken wings, animal skin and slow cooked cuts of beef.
Let's go through each to see what we are dealing with.
1. Bone Broth
Bone broth is the number one whole food source of collagen. I would argue you get more benefits from bone broth than collagen peptides because of extra electrolytes, vitamins and minerals in it.
You get up to 12 g collagen in one cup of bone broth. But you can't just buy anything off the shelf. You need one with at least 12 g protein per cup or serving.
You should also look for a low sodium version with less than 200 mg per cup. The best one on the market that ticks both of these boxes is the chicken bone broth powder from Bluebird Provisions. You can find it on Amazon Prime.
2. Small Fish (with a catch)
Like what I did there? The catch with eating fish is that they must be the small ones with the skin and tiny bones included in the tin like sardines, mackerel, anchovies or herring.
The best ones are the wild caught sardines made by Seasons.
Why is this the case? The skin and tiny bones have the most glycine, proline and gelatin mimicking amino acids. Larger fish that have the bones removed, unfortunately, give you none of these benefits.
And for god's sake, please eat the skin on you fish. This is like a multivitamin that is full of omega-3s and gelatin.
I know what you're thinking; they have a gross consistency and are full of calories I don't need. If anything is 'worth' eating for the calories, it is animal skin.
3. Chicken Wings and Feet
Chicken feet and wings with the skin on are a fantastic source of gelatinous amino acids. While feet taste a bit foreign to those of us in the West, they are incredibly popular in Asia.
And yes, chicken wings are delicious and have some nutritional benefit. Try to get ones that haven't been deep fried into oblivion with harmful vegetable oils.
4. Beef Oxtail
Beef oxtail is basically a portion of bone broth along with a gelatinous cut of meat. What more do you need? Not much in my opinion.
Slow cooked or 'tougher' cuts are meat are this way because of the collagen fibers cross linked in the meat. It takes hours for these fibers to cook out and tenderdize.
But the bonus is that you get a delicious meal that is full of collagen promoting amino acids.
5. Pork Rinds
If you're in a pinch, pork rinds (my favorite is EPIC) provide lots of glycine and other amino acids that are great for collagen production in the body.
What are the different types of collagen peptides?
The different types of collagen peptides range from Type I to Type V.
- Type I: Tightly packed in order to give our body its shape and structure (tendons, ligaments, skin and bones). This makes up 90% of our body's protein.
- Type II: Gives us joint support and provides connective tissue and cartilage.
- Type III: Commonly found in arteries, muscles and organs.
- Type IV: Makes up the layers in your skin.
- Type V: Found in the placenta and in the cornea of your eyes.
Most commercially available collagen brands are bovine sourced, which is a great source of type 1 and type 2. Marine collagen is also a good source of 1 and 2.
What happens when you take collagen peptides everyday?
If you take collagen peptides everyday, chances are that your digestion will get better, you will feel better, notice skin changes and maybe healthier joints after some time.
It takes up to 3-6 months in order to experience the true benefits. And you may not notice anything. It is important to keep your expectations in check. It is not a panacea... nothing is.
What does collagen peptides do to your face?
Collagen peptides can improve the hydration in the skin around your face and reduce some visible signs of aging like crow's feet. You need to get 10 g per day for 3-6 months in order to get these benefits.
How long does it take for collagen peptides to work?
Collagen peptides take between 3-6 months to work for skin health and joint pain benefits. Oftentimes you will get digestive benefits in as little as one week of regular use.
Blood sugar control and sleep benefits maybe immediate as well because of the mechanisms that make it work.
Is it better to take collagen peptides in the morning or evening?
Taking collagen peptides at different times of the day will give you different health benefits.
- For digestive health and blood sugar control, you are best to take it before your meals.
- For joint, tendon or ligament pain, you must take it one hour before you exercise along with 50 mg vitamin C.
- For skin and hair health, there is no time of day that is better. Just get it consistently in your diet.
Closing Thoughts
If you’re considering taking collagen peptides, I recommend using a non-GMO bone broth instead. Bone broth has more protein, hydration, hyaluronic acid, glycine, glutamine, glucosamine and chondroitin.
If you're looking to get started, try the bone broth powder from Bluebird Provisions. Their bone broth is made with pasture-raised, grass-fed beef and chicken bones that are slow-simmered for 24 hours. This results in a delicious and nutrient-rich broth that’s high in collagen peptides.
Have you tried collagen peptides? Did they work for you or not? Leave a comment and let me know.
Disclaimer: this information is for educational purposes only and has not been evaluated by the FDA or CFIA. It is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Please consult your primary care physician for advise on any of this.
Sources:
(1) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23949208
(2) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18416885
(3) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5793325/
(4) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12589194
(5) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21628872
(6) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27852613
Bluebird Provisions is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.














Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.