Animal Based Diet Pros and Cons: Is it Safe?
Animal Based Diet Benefits
Are you wondering if an animal-based diet is the right choice for you and your health? There are many potential benefits, but there are also some drawbacks that you should be aware of.
Many people believe that animal-based diets are unhealthy and can cause deficiencies in certain nutrients. However, with the proper planning, an animal-based diet can be safe and healthy for most people.
This guide will outline the pros and cons of animal-based diets and highlight the specific nutrients you might be deficient in.
Before we dive in, I'll mention that one of the best things you can add to an animal centric diet is a gelatinous bone broth to make sure you are getting enough amino acids.
One more quick note: this website is reader-supported. I spend a lot of time personally evaluating, testing and reviewing each product on this list. When you buy through links on our site, I may earn an affiliate commission.
What is an Animal Based Diet?
The Animal-Based Diet, a concept popularized by Dr. Paul Saladino, is an ancestral, nutrient-rich eating plan primarily focusing on consumption of animal foods. This diet combines aspects of primal, paleo and carnivore diets, emphasizing on:
- Nutrient-dense foods from ruminant animals like beef and bison.
- Incorporation of organ meats, which are extremely nutrient-rich.
- Complementary foods including fruits, honey and some squashes.
- About 50% calories from animal fats, 30% from animal proteins, and 20% from approved-carbs.

The diet does allow for some chicken and pork, but only those who are responsibly sourced and not fed gmo grains, corn or soy. The diet avoids vegetables to dodge the so called 'plant defense' chemicals in them.
Followers of this diet claim that vegetables can cause inflammation and lead to autoimmune issues. I'll get into that more below.
Animal-Based Diet Food List
Here's a list of 30 foods typically included in an animal-based diet:
|
Grass-fed beef |
Pasture-raised pork |
Pasture-raised chicken |
Wild game meat |
|
Organ meat |
Bone Broth |
Wild-caught fish |
Corn/soy-free eggs |
|
Raw, organic honey |
Raw cheese |
Raw milk kefir |
Banana, kiwis, pineapple, mango and papaya |
|
Avocado |
Beef Tallow, Chicken Schmaltz |
Grass-fed ghee |
Ceylon cinnamon |
Don't forget that you can customize these foods to your needs. If you prefer eating different fruits, then go ahead.
Meat and Protein Requirements
Here is how to calculate your meat and protein requirements on the animal based diet.
|
|
Low End |
High End |
|
Protein (g) |
Goal bodyweight multiplied by 1 |
Goal bodyweight multiplied by 1.2 |
|
Meat (lbs) |
Total protein intake divided by 100 |
Total protein intake divided by 100 |
For example, if your goal bodyweight is 200 lbs, you want to consume 200 to 240 grams of protein and 2 lbs of meat per day.
Organ Meat Requirements
The diet mainly recommends liver, but you can also consume heart, testicle, bone marrow, triple, kidney, spleen, pancreas, brain and intestines. Try to get 0.5 oz of liver daily or 2 to 3 ounces per week for best results.
Fruit and Honey Recommendations
Based on your activity level, you can figure out how many grams of carbs to consume per day. Note: these are to come from fruit and honey only.
|
How Active Are You Per Day? |
Low End Carbs (g/day) |
High End carbs (g/day) |
|
Low (0-3 hours) |
Goal bodyweight multiplied by 0.7 g |
Goal bodyweight multiplied by 0.9 g |
|
Medium (3-6 hours) |
Goal bodyweight multiplied by 0.8 g |
Goal bodyweight multiplied by 1.1 g |
|
High (6-12 hours) |
Goal bodyweight multiplied by 1 g |
Goal bodyweight multiplied by 1.5 g |
For example, if your goal bodyweight is 200 lbs and you are medium active, then you want to consume between 160 and 220 grams of carbohydrates per day.
How to Eat an Animal-Based Diet
You can eat an animal-based diet by focusing on nutrient dense parts of the animal, mild amount of fruit, squash and organ meats.
Here is an idea of how to get started today:
- Breakfast: of 2-4 eggs paired with things like sliced watermelon or cantaloupe. Or you can eat beef bacon and avocado.
- Lunch: ground lamb / bison burger, shrimp 'taco' or a grass-fed ribeye steak.
- Mid-day snack ideas: hard-boiled eggs, beef jerky or a mug of bone broth (I like Bluebird Provisions).
- Dinner: ribeye, pork chops or wild caught salmon.
Remember that these are just a few ideas to get you started. I have a complete food list below that will help you as well.
It is best to tailor the foods you eat to your needs. Don’t stress over minor deviations - it’s about what best suits your body and needs.
And if you feel like this way of eating is not completely serving you because it is difficult to adhere to or you are missing something, just eat that food.
Restrictive diets do not work in the long-term. This is more about creating lasting habits that can last throughout your life.
Animal Based Diet Benefits
The health benefits of the animal based diet are that you get high quality protein, more zinc, iron and B12, more omega 3 fats, lower carbs and sodium (if you want it), increased fullness, potential muscle growth, cost savings and gut health (for some people).

Woah Connor, that is a long list of benefits. Don't worry, I'll break each of these down for you below.
1. Higher (and Quality) Protein Intake
Of course you get more protein and can easily hit your daily protein target from eating mainly animal meat, but what some people miss is the superior quality of protein.
Since the diet focuses on eating nose to tail, you are consuming a wide variety of essential and non essential amino acids from organ meat and what I refer to as gelatinous meats.
Gelatinous meats are cuts that require low and slow cooking to break down all of the tough connective tissue. These meats are tough because they are full of collagen protein and other connective tissue.
This tissue turns to gelatin when cooked, which is why brisket or short ribs literally melt in your mouth.
Gelatinous meats are full of unique amino acids (glycine, proline and hydroxyproline), which we lack in your standard American diet.
Other benefits are that you get a range essential amino acids including leucine, isoleucine and valine. These are vital for muscle growth and repair.
2. Higher Iron, Zinc, Choline, Copper, Vitamin A and Vitamin B12 Intake
Iron, zinc, choline, copper, vitamin A and vitamin B12 are vital nutrients your body needs to function optimally.
Getting these from an animal-based diet allows your body to absorb them more effectively because they are in their whole food form.
Here are some of the vitamins and minerals you are prioritizing with an animal centric meal plan.
- Zinc: a mineral important for cell growth and development.
- Iron: a nutrient critical in maintaining a healthy immune system.
- Choline: crucial for brain development and function, fat metabolism and liver health.
- Copper: helps build red blood cells and supports immune function.
- Vitamin A: helps with immune responses and assists in white blood cell production.
- B vitamins like folate and B12, for staving off deficiencies that could weaken your immunity.
To give you an idea of how much of these you are getting, just 1 oz of a high quality beef liver gives you 250% of your daily B12, 125% for copper, 185% for Vitamin A and 50% for riboflavin.
If you don't like the taste, I recommend trying beef liver supplements. This way, you get the benefits without having to deal with the metallic taste.
You can also eat a few pasture raised eggs to get tons of Vitamin A, E, B12, choline and essential fatty acids.
3. Higher Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake
One major benefit of an animal-based diet is the higher intake of essential Omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients are often lacking in Western centric diets.
Omega 3s are potent anti inflammatories that are fantastic for brain health, reducing joint pain and eye health. If you are dealing with chronic health issues, omega 3s can help to decrease inflammation related to most diseases.
The added benefit of animal fats are that they are naturally rich in fat soluble vitamins like Vitamin A, D and K2 (also great for heart health).
An example is grass-fed butter, which has more Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins A and E compared to conventional (1).
We are talking about small overall values here, but every little bit helps in the grand scheme of things.
4. Lower Carbohydrate and Sodium Intake
Since animal protein has no carbs, and you are eating modest amounts of fruit, you will most likely be eating low carb an an animal-based diet.
You'll also likely be eating a lower sodium diet than a typical Western diet that is full of processed sodium bombs.

If you are struggling with blood sugar spikes, have type 2 diabetes, then this might be a good option. It is a much better one than gambling with the GOLO diet side effects.
There are a few potential benefits of reduced carbohydrate intake:
- Improved blood glucose control: This can be a definite plus if you're living with type 2 diabetes. Extended periods of high glucose levels can lead to even more chronic health issues.
- Reduced inflammation and weight gain: By cutting out processed carbohydrates notorious for causing inflammation and weight gain, you are setting yourself up for success.
A word of caution, if you are trying to do intense, endurance or cardio exercise; it is difficult to perform well without carbohydrates before, during and after.
Sure, you can become more fat adapted and do okay. But there is a reason why top endurance sports athletes (runners, cyclists, triathletes) all consume 60 to 120 grams of carbohydrates per hour in competition.
Because they are burning a lot of carbs during this type of exercise.
5. Increased Satiety
The animal-based diet can keep you feeling fuller for longer periods, potentially leading to weight loss.
This high-satiety is fullness benefits are thanks to quality protein and healthy fats found in animal foods.
So, how does it work? Well, when you consume high-fat and high-protein foods, your body feels satisfied quicker, which can prevent overeating.
But there are two other things at play here:
- You are also eating similar foods, which can lead to palate fatigue. So you will eat less because you are bored of it (2).
- You're spending more time chewing that you would on other diets, this also increases satiety (3).
For example, eating a steak will likely keep you satisfied longer compared to a diet high in processed foods, reducing your overall calorie intake.
6. Potential Benefits for Muscle Growth and Strength
Choosing an animal-based diet can do wonders for your muscle growth and strength. Why? Because you're getting the perfect fuel for muscles: high-quality proteins, essential nutrients and vitamins.
On an animal-based diet, the amount of protein you consume daily is largely determined by your goal body weight. For example, for every 100 lbs of your desired body weight, you should aim to consume at least 1 lb of meat per day.
And if we are talking about daily protein requirements, these range from 1 gram to 1.2 grams of protein per pound of goal bodyweight.
So if your goal bodyweight is 200 pounds, then you want to eat between 200 to 240 grams of total protein per day.
Getting this much protein will enhance muscle protein synthesis and make it easier for you to pack on muscle and strength... provided that you are lifting weights.
Just remember that these are rough guidelines based on the diet, your health status and personal goals.
7. Potential Benefits for Gut Health
An animal-based diet can be helpful for your gut health, and since the gut is the cornerstone of health, it could help you feel better elsewhere at the same time.
You're naturally eating more gut healing amino acids like glycine, proline and glutamine. Especially if you are drinking lots of quality bone broth or eating animal skin (pork rinds) or small fish with bones.
These amino acids help to build new connective tissue in your gut lining, which helps you digest and absorb food without bloating, gas or stomach pain.
I used to be sensitive to dairy and eggs, but after years of drinking bone broth, I can now tolerate both of them without issues because I fixed my gut.
The low carb nature of these diets also can help SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth) or candida.
8. Cost Saving
An animal-based diet can surprisingly be a cost-effective approach to nutrition. Here are a few reasons why:
- It helps reduce waste by utilizing byproducts to create more products (ex: bone broth), hence offering value for money spent.
- You can buy less expensive cuts of meat (roasts, stews, flanks, ribs) and batch cook them for the week. These are much more cost effective compared to muscle meats and processed foods.
- Lastly, though you'd spend more initially on purchasing high-quality animal protein, remember the nutritional and environmental benefits can make it worth the cost in the long run. Sticking to responsible, animal-based dieting can prove resource-efficient over time.
Cons of an Animal Based Diet
The cons of an animal based diet are a lack of carbohydrates, fruit and vegetables, less micronutrients which have the potential to lead to nutritional deficiencies, a lack of fiber, possible gut health issues and the fact that there is no peer reviewed literature on this way of eating.
Let's go through each of these in more detail.
1. Lack of Carbohydrates
An animal-based diet, is naturally low in carbohydrates, which are the body's preferred source of energy. The type of diet that Dr. Saladino recommends is one that that allows for some fruits and vegetables.
This will likely be enough carbohydrates to top off the glycogen stores for most people who are sedentary or doing non-intense forms of exercise.

That being said without the regular amount of carbs that your body is used to, your energy levels may dip, leading to fatigue.
Of course you can adapt to a higher protein and fat centric diet (much like intermittent fasting), but this does take some time.
You'll likely got though the keto flu (and all the nasty symptoms) while you body is getting accustomed to using fat for fuel.
Finally, if you are doing endurance exercise, exercising vigorously or playing sports that require sprinting, then you might struggle with the lack of carbs.
Sure, you can train your body to use fat for fuel, but you will not get the same performance as you would on a higher carb diet.
2. Lack of Vegetables
You're not getting vegetables while on a an animal based diet, and with that you are missing out on some crucial vitamins, minerals and nutrients like fiber, Vitamin C, Vitamin E. I'll get into the specifics below.
3. Lack of Micronutrients
If you're considering shifting to an animal centric diet, you must understand that you run the risk of micronutrient deficiencies. That's because certain vitamins and minerals are hard to get without vegetables.
The three main things to consider are fiber, Vitamin C and plant compounds. These can largely be avoided if you eat enough of the right fruits.
- Fiber: Animal-based foods are devoid of fiber, a crucial nutrient exclusively found in plant-based foods like oats, barley and vegetables. Missing out on fiber may increase cholesterol levels and up the risk of constipation, heart disease and colon cancer.
- Vitamin C: Meat, specifically cooked meat, virtually lacks vitamin C. Insufficient vitamin C intake could increase the risk of scurvy, poor wound healing and lead to tooth loss.
- Beneficial Plant Compounds: The carnivore diet omits beneficial plant compounds and antioxidants present in vegetables. These antioxidants are associated with reducing the risk of diseases like heart disease, Alzheimer’s and type 2 diabetes.
4. Potential for Nutritional Deficiencies
Even with all the benefits, an animal-based diet could potentially lead to micronutrient deficiencies as certain vitamins and minerals are harder to source solely from meat.
This deficiency could even lead to diseases like scurvy due to a lack of Vitamin C. There are a few other nutrients that are difficult to obtain from meat, which are magnesium, manganese and Vitamin B9.
That being said, if you are diligent and consume lots of organ meats long with the right types of fruit, you can do a really good job to address any of these possible deficiencies.
5. Lack of Fiber
Some animal based diets are low in fiber (unless you eat lots of fruit). Low fiber diets increase your risk of constipation, gut impingements or other gut issues including inflammation.
This is because fiber helps keep the intestines and bowels moving properly. Fiber also nourishes your gut with bacteria it needs to thrive. Without this bacteria, you might be at a higher risk of inflammatory gut issues like IBS and IBD.
Lower fiber diets also increase the risk of high cholesterol, heart disease and colon cancer.
6. Potential Risk of Digestive Issues
An exclusive animal-based diet can lead to unwelcome digestive issues for a few reasons.
- The diet is lower in fiber, which can lead to blockages and constipation. You can avoid this by eating lots of fruit and specifically raspberries and blueberries.
- Eating lots of animal products can increase the hormone IGF-1 in your body. This can cause inflammation in the gut (4).
- Depending on the type of meat your eat, it can produce more TMAO in your body. TMAO is a compound found in some meat that can potentially disrupt your gut microbiome, impacting overall health (5).
Ensure to carefully consider these potential digestive issues and make sure you are drinking lots of gut healing bone broth to avoid them.
7. Lack of Peer Reviewed Research
The last downside of an animal-based diet is the scarcity of peer-reviewed research on its benefits. This leaves several questions unanswered.
Firstly, we're missing data. There are no scientific studies examining the short or long term health effects of animal based nutrition.
Second, we're left to speculate. In the absence of concrete studies, the benefits are mostly deduced from personal stories, case studies and anecdotes. While these are great, they are not science.
Is an Animal Based Diet Safe?
An animal based diet may be safe for some people because it aligns with how our ancestors ate, however, there is no peer reviewed research on the diet, which is why some people consider it to not be safe for the general population.
If you are considering this diet, read this entire guide first and make sure to speak with a registered dietician if you have any other questions or concerns before getting started.
Who Should Consider an Animal Based Diet?
You might want to consider an animal based diet if you have SIBO, are looking for another weight loss option,
1. People with SIBO
If you are dealing with SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth), then an animal based diet might be a good solution because it can be very low carb. This will help manage your symptoms since the bacteria feed off carbohydrates.

Other people report decreases in bloating associated with FODMAP foods since the diet restricts those.
2. Those who are looking to lose weight
If you're looking to shed some pounds, consider trying an animal-based diet because it severely restricts the types of foods you can eat. We know from buffet studies that variety leads to weight gain, so you might find that this diet helps since you're only eating a few types of food (6).
Also, the diet helps to keep you satiated and feeling fuller for longer because it is high in fat and protein. This can lead to less calories throughout your day which could help with weight loss.
Finally, the diet discourages high calorie, processed foods, which are calorie bombs. Much of the obesity epidemic can be pinned on the availability of fast food, processed food and other foods that combine fat, sugar and salt.
Remember, though, severe calorie deficits, crash diets and the like can cause severe long-term health issues, so consulting a registered dietitian is advised.
3. People Looking to Eat More Whole Foods
An animal-based diet can be your alternative if you're looking to incorporate more whole foods. You are getting a lot of nutrient dense organ meats like liver, kidney and heart, combined with fruits and eggs.
By definition, this is truly a whole foods diet. But please make sure you do your research by reading the cons of the diet above.
4. Those who want to try a fad diet
You might be intrigued by the latest fad diets and considering an animal-based one, or even the carnivore diet. Here are the reasons why it could appeal to you:
- A new approach: As a diet trend, it might seem exciting and cutting-edge to participate in.
- Experimentation: Do you like to test or tinker with things? Then this diet might be a good fit for you to try.
With all these benefits and hype around this way of eating, I would be careful. I'm certainly not recommending this you, I'm merely giving you information so that you can make an informed decision.
This diet can be highly restrictive, and maintaining it for the long-term may not be manageable. It's also important to have a healthcare professional monitor your health if you decide to give it a try. There's no one-size-fits-all diet.
5. People who want to increase protein intake
If you want more protein in your diet, then this way of eating might be a good idea. you'll get at least 1 gram of protein per pound of goal bodyweight to make sure you are getting a balance of essential and non essential amino acids.
6. People who want more organ meats
If you're keen on increasing your organ meat consumption, going the animal-based diet route might be the best move. You'll be eating 2-3 ounces of organ meats per week if you follow the recommended guidelines.

7. Those who want more quality fats
You may have heard that animal fats are bad for your health, but the truth is a bit more complex. In fact, adding these to your diet could provide some essential fat soluble nutrients.
You are getting lots of quality Omega 3 and Omega 6 fatty acids on this diet. These are great for eye health, brain health, joints and reducing inflammation.
You can experiment with different types of fat that may be new to you like beef tallow, chicken schmaltz (fat) or grass fed ghee. These add delicious flavor combinations.
In fact, when I was making bone broth during the first few years of my business, I used to save the beef fat and chicken fat the solidifies on top of the broth, then render it down into tallow and schmaltz.
I started cooking everything using these two fats and my skin never looks healthier. The chicken schmaltz in particular had such a rich and delicious flavor.
It is not a surprise why it's used in many of the top dog foods on the market.
Food Sourcing
Sourcing food on the diet can be tricky because organ meats are hard to come by. Also, depending on the quality of meat you are after, it can be difficult and expensive to source as well.
We'd all love to only purchase grass fed and pasture raised animals, but that is not the reality for many of us. Due to your location and financial situation, it can be hard to figure out where to look and what you need to prioritize.
Organ meats like liver and kidney can be found in some large grocery stores in the meat section or in the freezer specialty meat section. More exotic organ meats like tripe and pancreas are likely more difficult to find.
Farmer's Markets Are Your Friend
I live in a town that has farmers markets, so I do my best to ask the farmers to bring organ meats the following week if possible. Because most of the time they will not bother to bring them to the market because they don't think anybody wants them.
Of course, if you are in a pinch getting organ meats, you can try beef liver supplements to get you nutrients covered.
As far as other meats go, I like to batch cook roasts or stews for the week. Then you at least have some meat to build your meals around. For this I like to use sirloin or blade roasts, which are cost effective and can be found in many grocery stores.
Of course, it is up to you in terms of what cuts of meat you use. If you are on the coast you can likely find more seafood and fish. I like to buy smoked oysters / mussels and canned sardines packed in water for convenient protein sources.
What are animal based diet side effects?
Animal based diet side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, constipation, headache, hydration issues from fluid loss, dizziness, fatigue and insomnia. Some of these will last a few days or some could last weeks.
Many of these are due to low electrolytes due to lower carbohydrates in your system. It always takes trial and error to figure out how many carbs you can get away with to function properly.
While you likely will not experience all of these (or perhaps any of them), I wanted to list all of the possibilities up front.
What is the Animal-Based 30?
The Animal-Based 30 (AB30) diet a 30 day meal plan where you eat animal products, including meats and organs that runs every January.
In reality, it is not quite as restrictive as it may seem. They recommend trying to eat 80 to 90% animal based foods, depending on your comfort level.
You can also incorporate other foods based on their own internal toxicity level. For example, 'Low Toxic Foods' include beef, chicken and raw honey, while 'High Toxic Foods' include brown rice and chocolate.
Closing Thoughts
If you're thinking about trying an animal-based diet, it's important to do your research and consult with a doctor or registered dietitian to make sure it's safe for you.
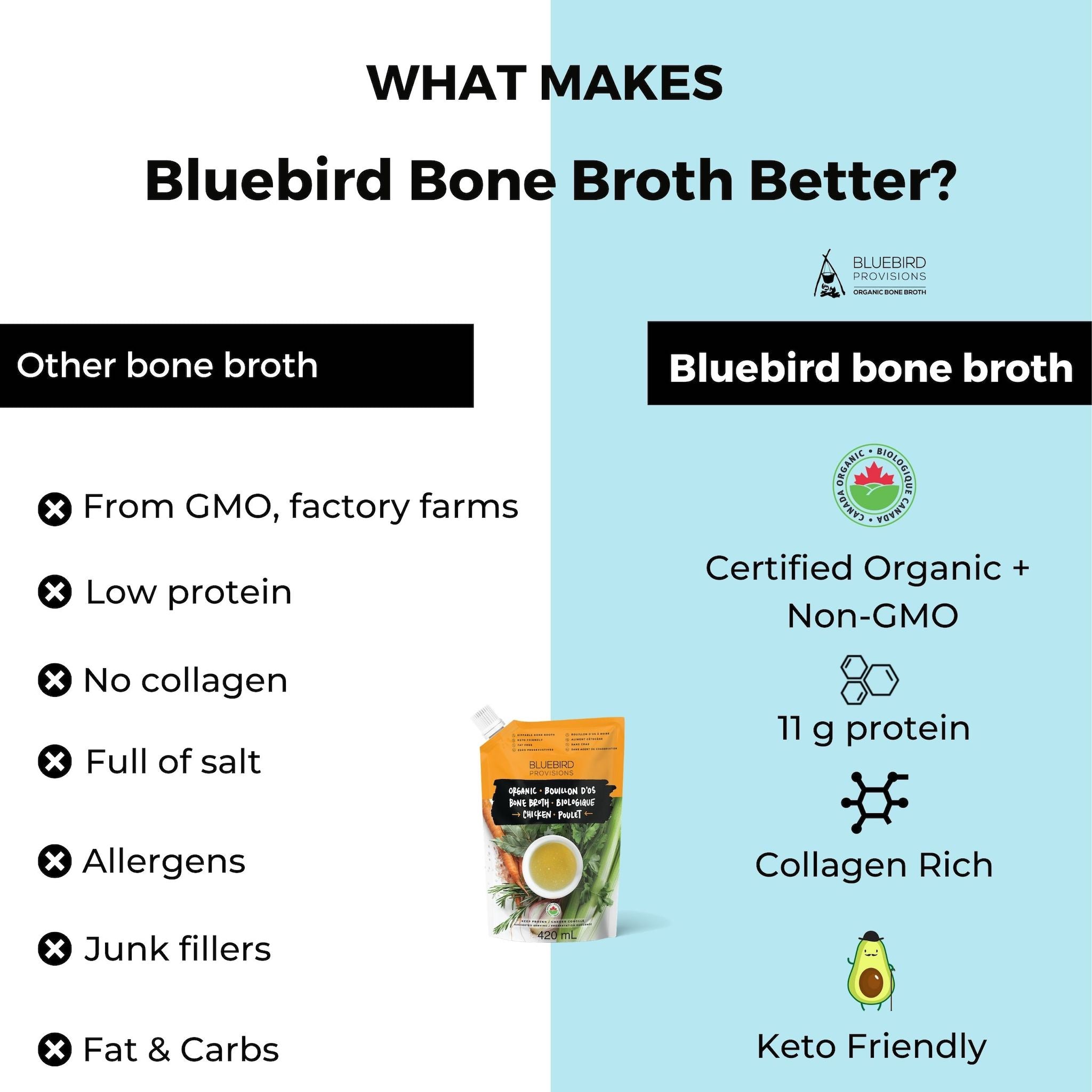
There are potential benefits and drawbacks to consider and you'll need to make sure you're getting enough of the right nutrients. If you are going to give it a try, make sure have a high quality bone broth for gut health.
My favorite is the chicken bone broth powder from Bluebird Provisions.
Have you tried this diet? Or do you have any questions for me? Leave a comment and I will get back to you.
Bluebird Provisions is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35028571/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36225863/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26188140/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12433724/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7074160
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36645103
Disclaimer: this information is for educational purposes only, is not medical advise and has not been evaluated by the FDA or CFIA. It is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or healthcare issue. Please consult your primary care physician for advise on any of this.














Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.